Question
Question: The image for the converging beam after refraction through the curved surface(in the given figure) i...
The image for the converging beam after refraction through the curved surface(in the given figure) is formed at.
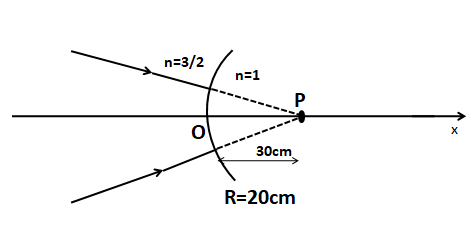
(a) x=40cm
(b) x=340cm
(c) x=−340cm
(d) x=7180cm
Solution
Use the equation for the refraction of light on a convex surface. The equation consists of the refractive indexes of the mediums. Put the values of given refractive indexes and the distance of the object from the surface. By this calculation, the image distance from the surface can be found.
Formula used: For the two mediums of refractive indexes of μ1 and μ2, if the light beam falls on a convex surface from a distance u and makes an image at distance v ,
the equation for the refraction of light on a convex surface will be,
vμ2−uμ1=Rμ2−μ1 , R is the radius of curvature.
Complete step-by-step solution:
When an object is placed at a distance u from a convex surface, the light refracts on this curve and thus an image of this object is made at a certain distance from the surface. Let, the image distance from the convex surface is v.
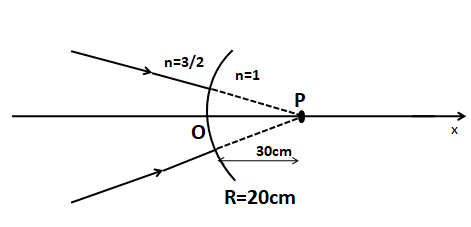
Let, the refractive indexes of the two mediums from which to which the light goes, are μ1 and μ2.
The equation for the refraction of light on a convex surface will be,
vμ2−uμ1=Rμ2−μ1
Given that, μ2=1[since it is given n=1]
μ1=23[since it is given n=3/2]
u=30
R=20
Now, from vμ2−uμ1=Rμ2−μ1
By putting the values given, we get from the above equation
⇒v1−3023=201−23
⇒v1−2×303=−401
⇒v1=201−401
⇒v1=401
⇒v=40
So the distance of the image here v=x
And the calculation we get, ⇒v=40
Option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: The beam of convergent light rays is when the rays return from completely different directions that finally meet at a selected purpose, then that collection of the rays is known as convergent rays or convergent beams of light. This happens in convex surface incidence.
Divergent is the opposite of merging light. This happens for concave surface incidence.
