Question
Question: The hybridization of atomic orbitals of central atom ‘Xe’ in \[Xe{O_4}\] , \[Xe{O_2}{F_2}\] and \[Xe...
The hybridization of atomic orbitals of central atom ‘Xe’ in XeO4 , XeO2F2 and XeOF4 respectively:
A. sp3 , sp3d2 , sp3d2
B. sp3d , sp3d , sp3d2
C. sp3 , sp3d2 , sp3d
D. sp3 , sp3d , sp3d2
Solution
Hybridization can be understood as mixing of orbitals of a given chemical species to form new orbitals. These new orbitals are known as hybrid orbitals. These newly formed hybrid orbitals have different energy levels, shapes, etc. as compared to the original orbitals it is made from.
Complete step by step answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
To determine the hybridization and shape of the given molecule, we must follow these steps:
Draw the Lewis structure to understand the rough structure of the given molecule and its bonding pattern. We can use the valence electron concept to make the Lewis structure.
After that, we must calculate the number of sigma bonds in the given compound. Sigma bonds can be understood as the single bonds which form the basic skeleton while bonding.
Following which, we must calculate the number of lone pairs. We can either count the number of lone pairs present in the Lewis structure or we can calculate the number of lone pairs using the formula: 2v−b−c , where v is the number of valence electrons, b is the total number of bonds and c is the charge on the atom.
We must now calculate the steric number. The formula for steric number is:
Steric number = (number of sigma bonds) + (number of lone pairs)
Now, the final step includes to correlate the steric number calculated to the following chart:
| Steric number | hybridization | Structure |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | sp | Linear |
| 3 | sp2 | Trigonal planar |
| 4 | sp3 | Tetrahedral |
| 5 | sp3d | Trigonal bipyramidal |
| 6 | sp3d2 | Octahedral |
| 7 | sp3d3 | Pentagonal bipyramidal |
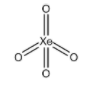
A. XeO4 :
There are 4 sigma bonds present in this molecule and no lone pairs are present on the Xe atom. Hence, the steric number can be calculated to be (4+0) = 4. Hence, the hybridization is sp3
B.XeO2F2 :
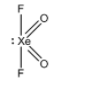
There are 4 sigma bonds present in this molecule and one lone pair is present on the Xe atom. Hence, the steric number can be calculated to be (4+1) = 5. Hence, the hybridization is sp3d
C. XeOF4 :
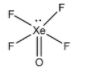
There are 5 sigma bonds present in this molecule and one lone pair is present on the Xe atom. Hence, the steric number can be calculated to be (5+1) = 6. Hence, the hybridization is sp3d2 .
Hence, Option D is the correct option.
Note:
Hybridization lets us explain the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory. This theory helps us to predict the geometrical structures of individual molecules on the basis of the number of pairs of electrons that surround the central atoms.
