Question
Question: The hybridisation of carbon in diamond, graphite and acetylene is respectively: (...
The hybridisation of carbon in diamond, graphite and acetylene is respectively:
(A).sp3, sp, sp2
(B).sp, sp2, sp3
(C).sp3, sp2, sp
(D).sp2, sp3, sp
Solution
Diamond forms a covalent and cubic structure with small tetrahedron units. Graphite exists in layers with hexagonal rings. The IUPAC name of acetylene is ethyne and the suffix (-yne) shows that it is an unsaturated compound.
Complete answer:
We should start by seeing these 3 compounds individually.
-We should know that graphite and diamond, both are very stable allotropes of carbon. But graphite is the most stable.
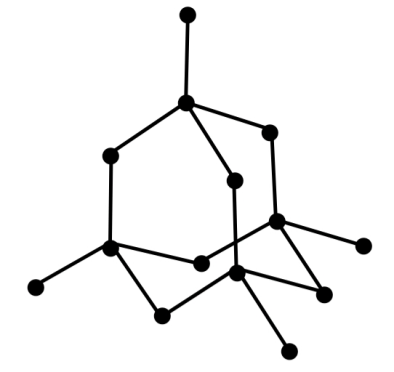
-Let’s talk about diamond first. Diamond is an allotrope of carbon which forms a giant covalent and cubic crystal structure by forming a repeating pattern of 8 atoms. All the carbon atoms in diamond form strong chemical bonds with other 4 carbon atoms which makes a perfect tetrahedron structure in the entire diamond structure.
Since each carbon atom is forming 4 strong sigma bonds, one with each of the 4 other carbon atoms, its hybridisation will be sp3.
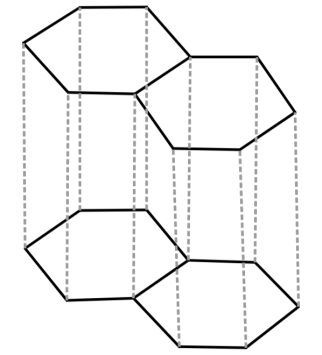
-About graphite we already know that it is the most stable allotrope of carbon. Graphite forms a giant covalent structure where every carbon atom forms 3 strong sigma bonds, one with each of the 3 other carbon atoms. This means that every carbon atom is bonded with 3 other carbon atoms. These carbon atoms form layers of hexagonal rings. Although these layers are attached to each other by weak forces.
Since here every carbon atom is attached to 3 other carbon atoms, the hybridisation of C is sp2.
-Now let us see acetylene. Acetylene is an organic compound with a molecular formula of: C2H2 and its IUPAC name is ethyne. It is an unsaturated compound. Here the 2 carbon atoms are attached to each other via a triple bond (1 sigma bond and 2 pi bonds). Hence the hybridisation of acetylene will be sp.

-So, the correct option is: (C)sp3, sp2, sp.
Additional information:
Carbon has the ability to form 8 different types of allotropes. All have different structures, hardness, properties, etc. On one hand where graphite is very soft due to its layered structure, while on the other hand diamond is very difficult to break and is used to cut glass.
Note: Remember acetylene is not the IUPAC name, it is a common name. Sometimes we just see the suffix (–ene) and assume the compound to be having a double bond and so sp2 structure. This is false since the IUPAC name is ethyne.
