Question
Question: The Heinsberg test of a \[C{}_5{H_{14}}{N_2}\] compound produces a solid that is insoluble in 10% aq...
The Heinsberg test of a C5H14N2 compound produces a solid that is insoluble in 10% aq. NaOH. This solid derivative dissolves in 10% aq. H2SO4 Sat. Which of the following would best fit these facts?
A.
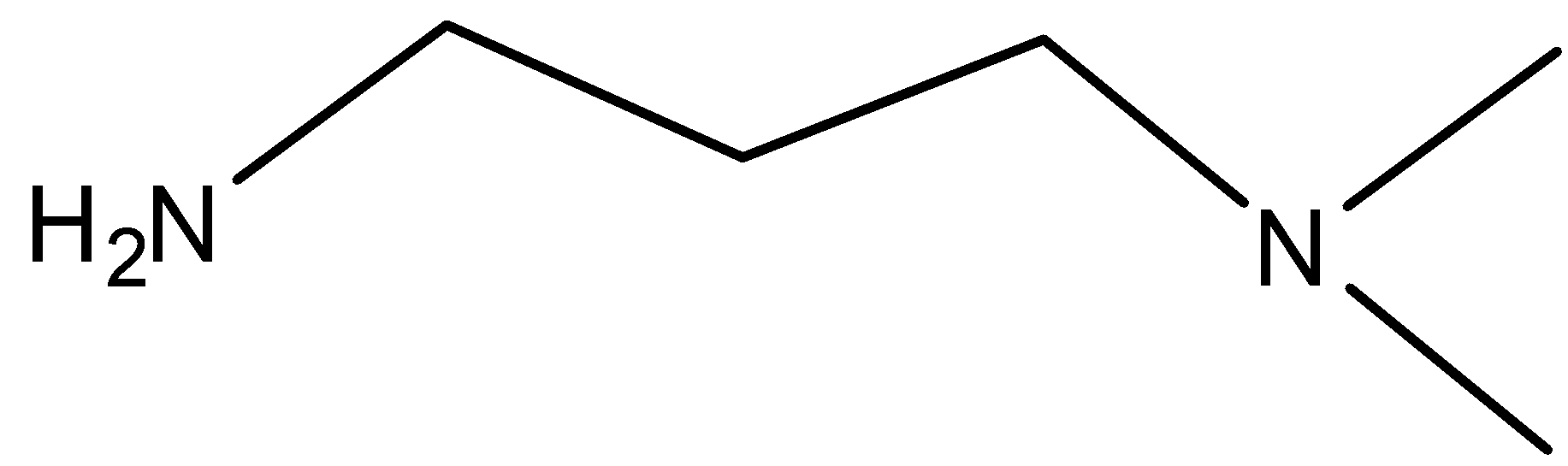
B.
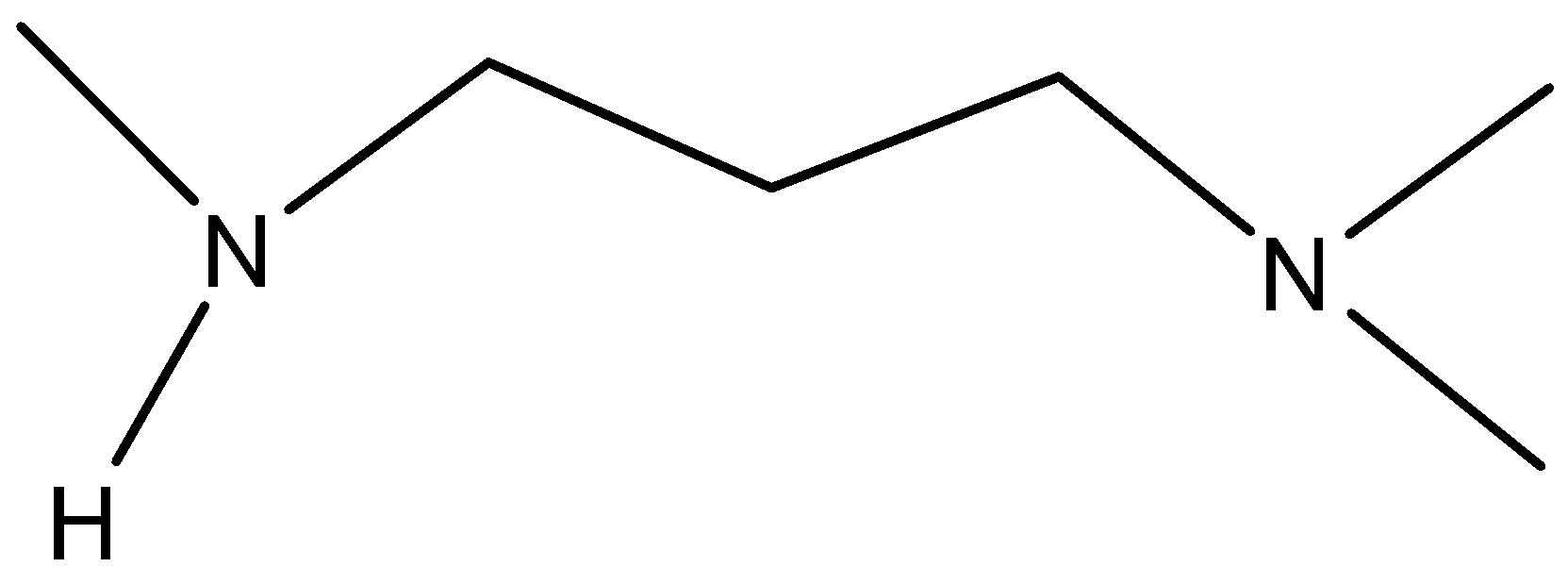
C.
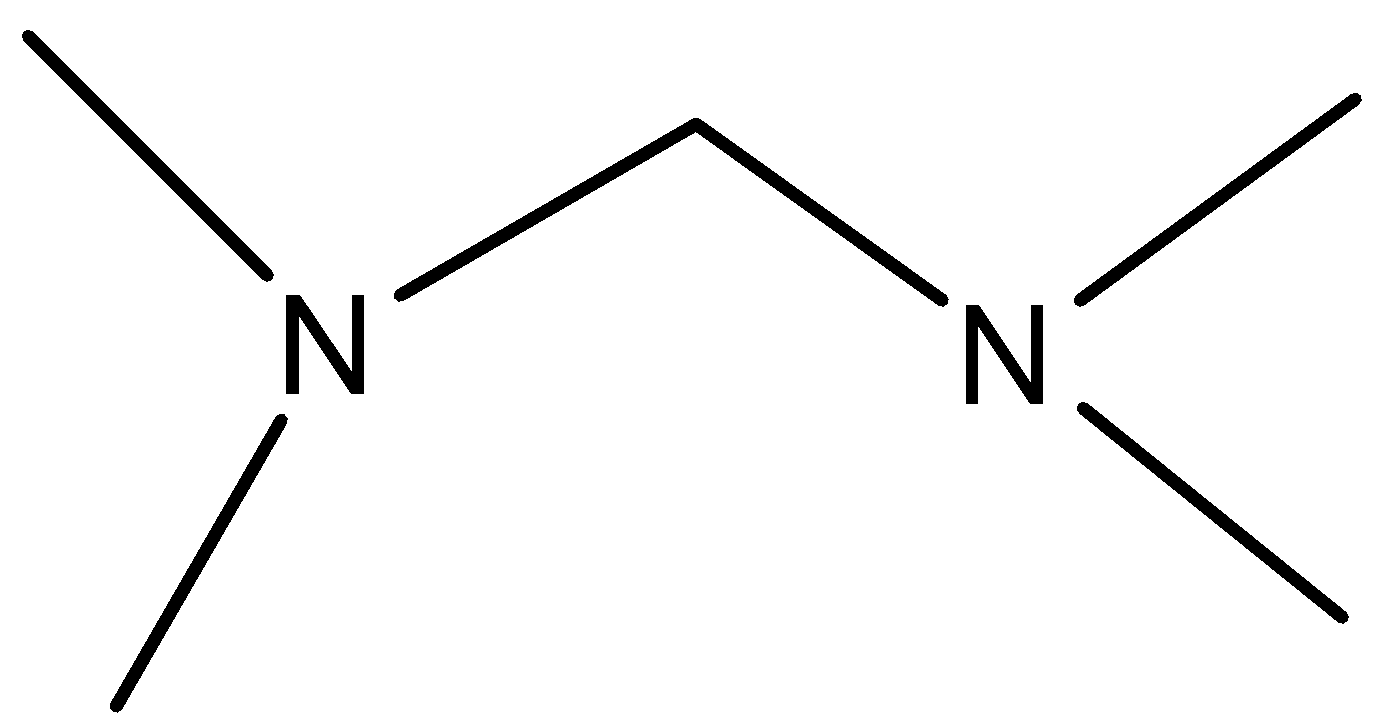
D.
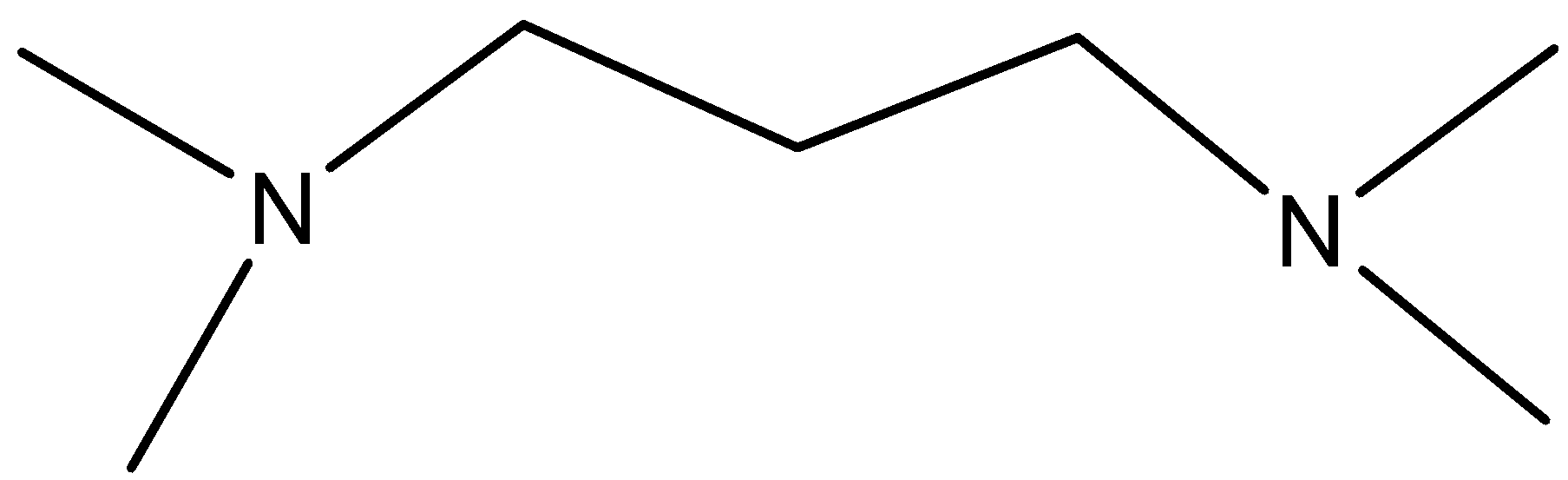
Solution
Heinsberg tests are used to differentiate between primary amine, secondary amine, and tertiary amine. Here reagent of this reaction is phenyl sulfonyl chloride. A reagent can be a substance or mixture of compounds which are used in chemical analysis or reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
The derivatives of amine are formed by substituting the hydrogen atoms that are attached to the nitrogen. This makes the nitrogen either 1 – degree, 2 – degree, or 3 – degree depending on the number of hydrogens that have been substituted. Here, C6H5NH2 is a primary amine or 1-degree amine and C6H5NHCH3 is a secondary amine or 2-degree amine.
To distinguish one from another use reactions where a change of physical characteristics has happened. For example, change of color of the solution, precipitation takes place, generation of effervescence, generation of different odors, etc.
According to this Heinsberg test, the phenyl sulfonyl chloride reacts with amine first. after this adding NaOH. it forms a sodium salt which is soluble in water. But for this reaction, at least two hydrogens should be present in the structure of the amine. Therefore, primary amine gives this reaction as follows,
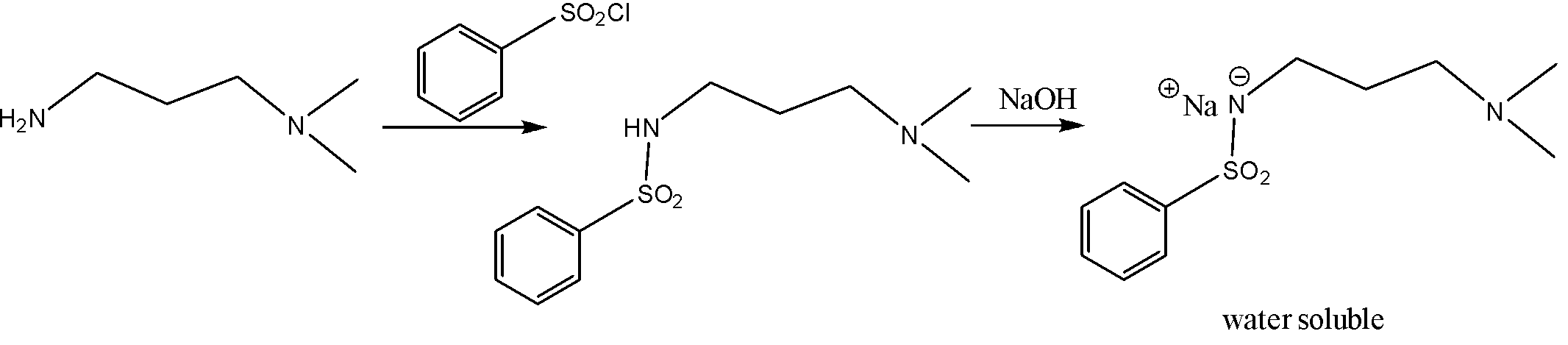
But in the case of a secondary amine, the formation of sodium salt is not possible. So, it cannot be soluble in 10% aq. NaOH. but it can be water-soluble in 10% aq. H2SO4 . As follows,
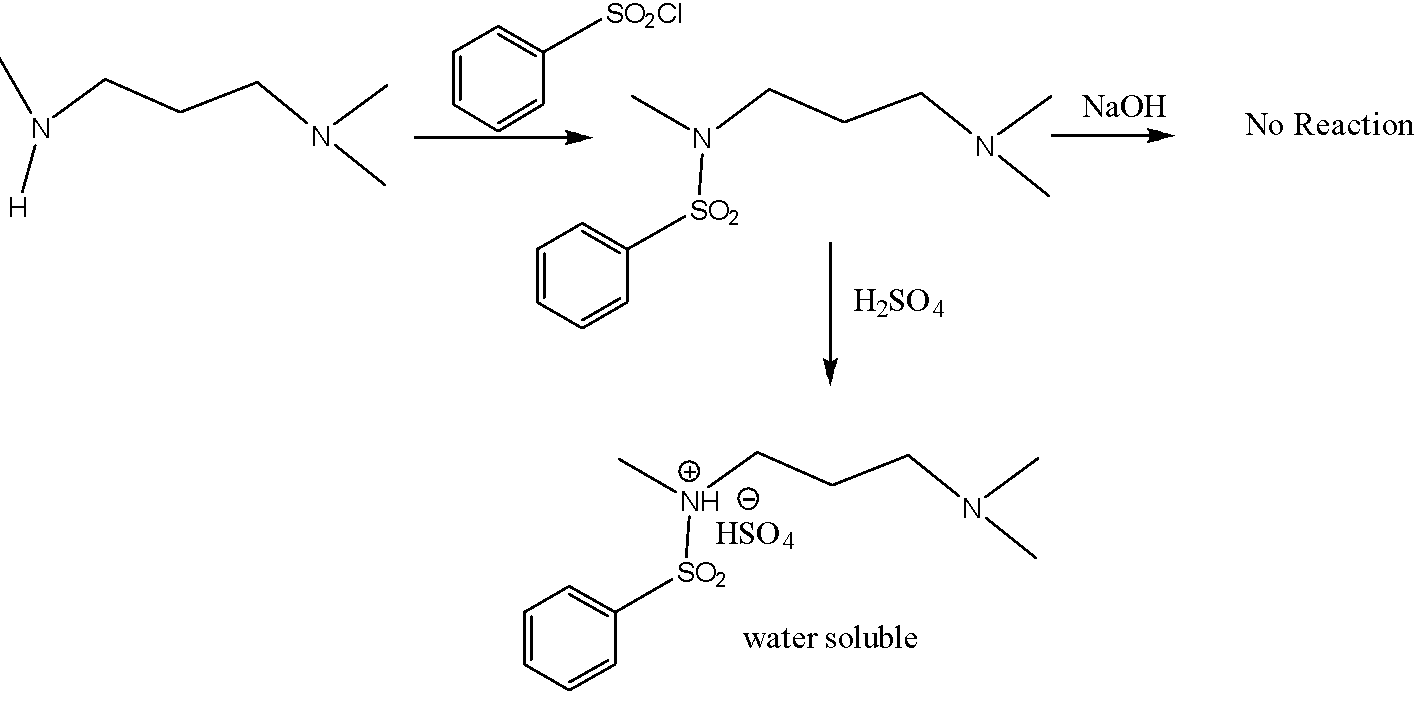
So, these facts are applicable to option B.
So, the correct option is B.
Note: The terms primary, secondary & tertiary are used to classify amines in a completely different manner than they were used for alcohol or alkyl halides. When applied to amines these terms refer to the number of alkyls (or aryl) substituents bonded to the nitrogen atom, whereas in other cases they refer to the nature of an alkyl group.
