Question
Question: The heat of hydrogenation of benzene is \[51\,kcalmo{l^{ - 1}}\] and its resonance energy is \[36\,k...
The heat of hydrogenation of benzene is 51kcalmol−1 and its resonance energy is 36kcalmol−1. What will be the heat of hydrogenation of cyclohexene?
A.18kcalmol−1
B.29kcalmol−1
C.50kcalmol−1
D.26kcalmol−1
Solution
Heat of hydrogenation: It is the amount of heat required by an unsaturated compound to get converted into a saturated compound by the addition of excess hydrogen. It is always exothermic in nature and represents the strength of carbon-carbon double bond in an alkene.
Complete answer:
Given data in the question:
Heat of hydrogenation of benzene =51kcalmol−1
Resonance energy of benzene =36kcalmol−1
As we know, there are total of three double bonds in a benzene i.e., C6H6 molecule, so three moles of hydrogen i.e., H2 are required to convert it into cyclohexane (C6H12). The reaction proceeds as follows:
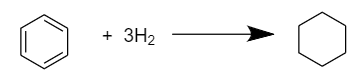
As the double bonds in the benzene ring are in conjugation and show resonance so, the actual heat evolved in the hydrogenation of benzene to form cyclohexane will be equal to the sum of heat of hydrogenation of benzene and its resonance energy.
Actual Heat of hydrogenation =51+36
⇒ΔHhyd=87kcalmol−1
Now, to calculate the heat of hydrogenation for cyclohexene (C6H10), we need to reduce only one double bond i.e., only one mole of hydrogen is required to convert it into cyclohexane(C6H12). The reaction proceeds as follows:
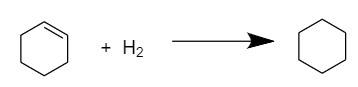
Therefore,
heat of hydrogenation of cyclohexene=3heat of hydrogenation to reduce three double bonds
⇒ΔHhyd=387
⇒ΔHhyd=29kcalmol−1
Hence, the value of heat of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is 29kcalmol−1. Thus from the given options, the option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:
Resonance energy: It is the amount of extra energy that a molecule gains due to extra stability experienced by the presence of a conjugated double bond system. Therefore, while calculating the heat of hydrogenation of a compound that consists of resonance, the resonance energy should be added to the expected value of enthalpy of hydrogenation.
