Question
Question: The graphical representation of vapour pressure of two components systems as a function of compositi...
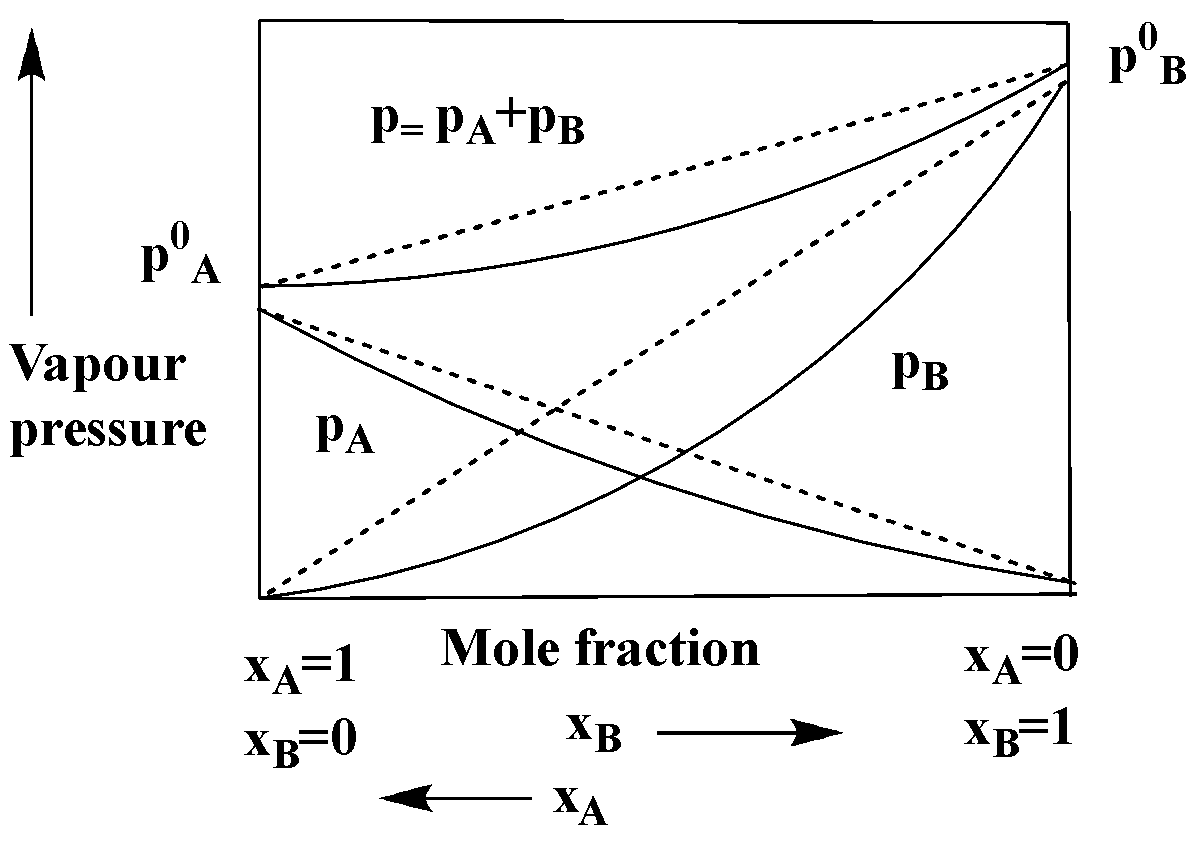
The graphical representation of vapour pressure of two components systems as a function of composition is given alongside. By graphic inspection, answer the following questions: What type of azeotrope will this system form, if possible?
Solution
An azeotrope or a seamless boiling purpose mixture could also be a combination of two or additional liquids whose proportions cannot be altered or modified by simple distillation. This happens when an azeotrope is boiled, the vapour has identical proportions of constituents as a result of the unboiled mixture.
Complete step by step answer:
As a result of their composition being unchanged by distillation, azeotropes are also known as constant boiling purpose mixtures. Some azeotropic mixtures of pairs of compounds are known and plenty of azeotropes of three or additional compounds are also known. In such a case it's infeasible to separate components by fractional distillation.
There are two styles of azeotropes: minimum boiling azeotrope and most boiling azeotrope. A solution that shows a bigger positive deviation from Raoult's law forms a minimum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition. For example, water mixture (obtained by fermentation of sugars) on fractionation yields a solution containing at the foremost 92.2% by volume of alcohol.
Once this composition has been achieved, the liquid and vapour have the identical composition, and no separation happens. A solution that shows massive negative deviation from Raoultˈs law forms a maximum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition. Nitric acid and water is an example of this category of the azeotrope. This azeotrope has an approximate composition of 68% acid and 32% water by mass, with a boiling purpose of 393.5K .
This system in the graph above will form a maximum boiling azeotrope as the system shows a negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
Note: Raoult’s law is considered to be a law of chemistry, with implications within the thermodynamics, it states that the partial pressure of each element of an ideal mixture of liquids is said to be equal the multiplication of mole fraction and the vapour pressure of the component within the mixture taken. In the result of that, the mole fraction of the solute in the solution is equal to the relative lowering of the vapour pressure of a dilute solution of a non-volatile substance.
