Question
Question: The given pair are: - 
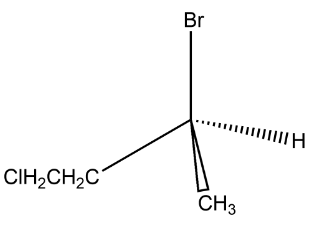
(A) Enantiomers
(B) Diastereomers
(C) Homomers
(D) Constitutional isomer
Solution
now the above given compounds have chlorine to be placed with two different alkyl groups attached to the centre carbon. As the structure of the molecule only changes due to the position of the functional group therefore the isomers given above have to be constitutional isomers.
Complete answer:
First before answering anything, we need to understand exactly what isomers are.
Isomers are defined as the two or more compounds having the same number of atoms but different structural or molecular formulas. The physical properties and the chemical properties of these substances are quite different from each other.
Isomers having the same number of atoms can be further divided into other categories. One of the categories is geometrical isomerism and the other is optical isomerism.
Now in geometrical isomerism what happens is that the number of atoms are the same but their geometry or position of the alkyl group or the functional group or the shape of the isomer is different from the other. These isomers are further divided into various parts depending on what type of geometrical change it has.
In optical isomers what happens is that the number of atoms is the same between the two or three compounds and also their geometry is am but what differentiates the two or three compounds is their optical resolution. This is a very difficult difference to observe which can be observed by passing light through it and the deviation it causes to the light.
In the above given compound what happens is that the chlorine group is first attached to the methyl group attached to the centre carbon while in the second compound what happens is that the chlorine is attached to the ethyl group, therefore the position of the chlorine atom is different and therefore the structure is different.
Therefore, the isomerism observed is constitutional isomerism.
Option (4) constitutional isomers.
Note:
Optical isomers are further divided into enantiomers, diastereomers and homomers. Enantiomers are defined as the optical isomers which are the non-superimposable mirror image of each other while diastereomers are those which are superimposable mirror images of each other.
