Question
Question: The given figures are of the human larynx, front view (i) and vertical section (ii). Identify the la...
The given figures are of the human larynx, front view (i) and vertical section (ii). Identify the labelled parts A to D.
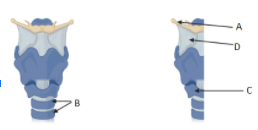
A. (A )- Glottis, (B) - Larynx, (C) - Vocal cord, (D) - Cartilaginous rings of the trachea
B. (A) - Epiglottis, (B) - Cartilaginous rings of the trachea, (C) - Trachea, (D) - Larynx
C. (A) - Glottis, (B) - Cartilaginous rings of the trachea, (C)- Larynx, (D )- Trachea
D. (A) - Epiglottis, (B) - Bony rings of the trachea, (C) - Larynx, (D) - Trachea
Solution
Larynx is an organ situated at the top of the neck which is involved in the process of breathing, protecting the trachea against food aspiration and producing sound. The larynx is commonly referred to as a voice box.
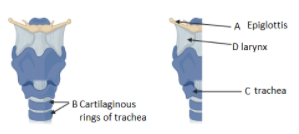
Complete answer: Larynx is located just below where the pharynx is split into oesophagus and trachea. The larynx consists of vocal cords and regulates the function of manipulation of pitch and volume that is essential for phonation. In the front view larynx, the cartilaginous rings of trachea are represented by label B. These cartilaginous rings of trachea are C shaped and provide support to the trachea. In the vertical section of the larynx, we can see epiglottis represented by label A. Epiglottis is elastic cartilage and a flap-like structure that guides the passage of both food and wind. The larynx which is labelled by D is further attached to the trachea allowing the passage of air into the lungs which forms a part of the human respiratory system. The trachea is also called windpipe. It is labelled by C. Therefore, (A)- Epiglottis, (B)- Cartilaginous rings of the trachea, (C)- Trachea, (D)-Larynx.
So, option B is the correct answer.
Note: The epiglottis guards the opening of both larynx and pharynx. During the swallowing of food, the epiglottis closes the opening of the larynx. The loudness of sound also depends on the strength of the expiration. Larynx plays an important role in the function of protection by preventing the entry of foreign particles in the lungs by reflexive actions and coughing.
