Question
Question: The geometry of \[{H_2}S\] and its dipole moment are: A.Angular and non- zero B.Angular and zero...
The geometry of H2S and its dipole moment are:
A.Angular and non- zero
B.Angular and zero
C.Linear and non-zero
D.Linear and zero
Solution
We need to find the geometry and hybridization of H2S molecules. We can find the hybridization by knowing the number of sigma bonds and lone pairs. Geometry of a molecule can be explained by the arrangement of lone pair and bond pairs
Complete step by step answer:
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals with different energies, shapes etc, that are suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory.
z=no.ofσbond+l.poncentralatom
Where, No. of σbond means single bond and l.p is the lone pair present on the central atom.
For value we have to see the following table.
| Z | Hybridisation |
|---|---|
| 2 | Sp |
| 3 | Sp2 |
| 4 | Sp3 |
| 5 | Sp3d |
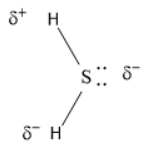
For H2S,
Z = 2 + 2
Z = 4
H2S will have Sp3hybridization and bent molecular geometry and also, H2S is a nonpolar molecule.
H2S molecule has an angular geometry because there are two lone pairs of electrons present that make the molecule bend.
As we can see that H2S is a bent molecule, so the dipole moment is non- zero because sulphur is more electronegative than hydrogen and makes the molecule slightly polar.
The Vectorial sum of the bond dipole moment will produce a non- zero total dipole moment.
Since the permanent dipole moment is non- zero H2S will show dipole-dipole interactions.
The bond dipole moment uses the idea of electric dipole moment to measure the polarity of a chemical bond within a molecule. It basically occurs when there is a separation of positive and negative charges.
Thus, the geometry of H2S and its dipole moment are Angular and non- zero.
Note:
Geometry of a molecule can be explained by the arrangement of lone pair and bond pairs while shape can be explained by the arrangement of atoms around the atoms, it is not linked with lone pair and hence only deals with bond pairs.
