Question
Question: The gene of interest is cloned at which position in plasmid pBR322 to facilitate quick selection?...
The gene of interest is cloned at which position in plasmid pBR322 to facilitate quick selection?
Solution
Extrachromosomal DNA, which is a small, circular, double stranded DNA molecule and occurs outside the cell’s chromosomal DNA. These naturally exist in most bacterial cells.
Complete Answer
One of the most used E. coli cloning vectors is pBR322. Plasmids are extra chromosomal, circular, autonomous, small, self-replicating pieces of DNA. These are usually seen in bacteria and their replication is not under the control of chromosomal DNA. The gene of interest is incorporated at the restriction enzyme site found in one of the selectable marker gene or antibiotic resistance genes. The restriction sites are EcoRI, BamHI, Hind III, Sal I, Pvu II, Pst I, Cla I and the selectable markers are TetR and AmpR.
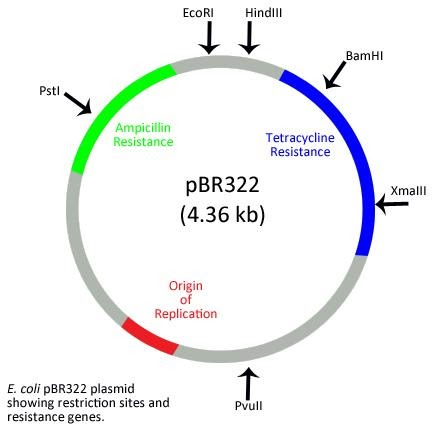
In length, pBR322 has 4361 base pairs and 2 antibiotic resistant genes mainly ampicillin and tetracycline resistant genes. The plasmid contains exclusive restriction sites for more than forty different restriction enzymes. Of all the restriction sites, eleven lies within the tetracycline gene while the ampicillin gene has only six key restriction sites.
Note:
Due to the ability of plasmid to replicate independently, they are used as a cloning vector in recombinant DNA technology for manipulating and transferring genes. In a bacterial cell, plasmids are transferred from one cell to another by a method called conjugation. The term plasmid was coined by Joshua Lederberg. This plasmid was created in the year 1977 by Bolivar and Rodriguez hence the name pBR322. Even though many other artificial plasmids were constructed, pBR322 is still one of the most popular cloning vectors used.
