Question
Question: The gene for blue eyes (b) is recessive to the gene for brown eyes (B). The following figure is give...
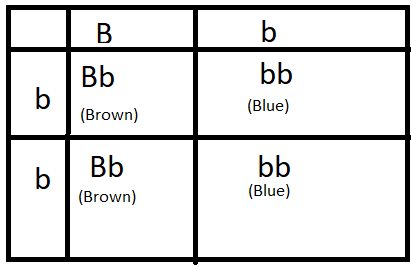
The gene for blue eyes (b) is recessive to the gene for brown eyes (B). The following figure is given: what is the % of individuals with brown eyes and blue eyes respectively?
Solution
The genetic crossing is the crossing over of two individuals to produce offspring. There are two types of crosses: monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross.
Complete answer:
George Mendle was the first mathematician to determine an unknown genotype by crossing over. Crossing over is the crossing over of genetic material among two individuals.
Types of traits in a cross: dominant trait and recessive trait.
Dominant trait: The gene which decides the appearance of an organism in presence of another trait is called a dominant trait.
Recessive trait: It is a weak trait that has no effect on organism phenotype in heterozygous cross.
Type of individuals: heterozygous (having two different gene as Tt/Bb) and homozygous (both gene are same as TT/tt/BB/bb)
According to the question BB is brown eye and bb is blue. B is dominant over b. so in presence of B (brown gene) b(blue gene wont express).
F1 generation has bb (blue) Bb (Brown) Bb (brown) bb (blue) so Brown eyed 50% and Blue eyed 50%.
Here is a diagrammatic representation of the cross
Note:
Monohybrid cross: crossing of two individuals that involve a single trait example height, colour, size etc. The mendelian ratio for monohybrid cross for F2 generation is 3:1.
Dihybrid cross: crossing over of two individuals that involves two traits for example height and colour of the flower. The mendelian ratio for dihybrid cross for F2 generation is 9:3:3:1.
