Question
Question: The function of IgE is * A. Mediate in an allergic response * B. Activation of B-cells...
The function of IgE is
-
A. Mediate in an allergic response
-
B. Activation of B-cells
-
C. Protection from inhaled and ingested pathogen
-
D. Stimulation of the complement system, passive immunity to the foetus
-
E. Present on lymphocytes surface as receptors
Solution
IgE is the immunoglobulin E which is synthesised by the plasma cell. IgE present in mammals only. It is associated with allergic reactions.
Step by step answer: The IgE antibodies have ε- heavy chains in them. IgE has a valency of 2, which means that they are found in the form of monomers only. These antibodies are found only in mammals.
IgE is the least abundant immunoglobin in the serum. IgE is expressed on the surface of the mature B-cells. These are synthesized by the plasma cells. The function of the IgE is to protect against several types of allergies by triggering a hyper allergen response. This prevents the body from going into an anaphylactic shock. Thus, IgE function to mediate in an allergic response.
Hence option A is correct.
Additional Information: There are five types of antibodies that are formed in our body. These are classified based upon the chains present in them.
1. IgA – These antibodies have α- heavy chains in them. IgA can have a valency of 2,4,6, or 8, which means that they are found in the form of monomers, dimers, trimers, and tetramers respectively. The trimers and tetramers are very rare and the dimers are very common.
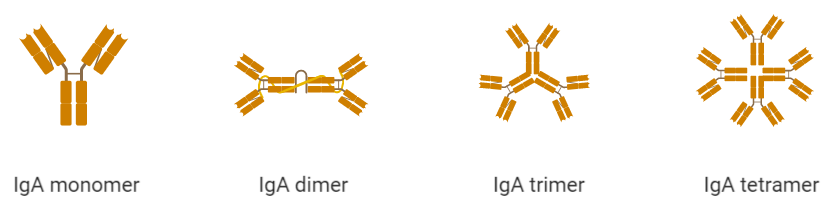
IgA is the second most common human immunoglobulin found in the serum. It is secreted in milk. It is also a common immunoglobulin in secretions like saliva, tears, and mucous. The function of the IgA is to protect the mucous membranes. It also activates the complement pathway when aggregated.
IgD – We know that these antibodies have δ- heavy chains in them. IgD has a valency of 2, which means that they are found in the form of monomers only. IgD is found at very low levels in the blood serum. IgD is expressed on the surface of the mature B-cells. The IgD works along with the IgM to help in the development of the B-cells. It does not activate any complement pathway.
IgG – These antibodies have γ- heavy chains in them. IgG has a valency of 2, which means that they are found in the form of monomers only.
IgG is the most common human immunoglobulin found in the serum. IgG is the only human immunoglobulin that passes from the mother to the foetus and provides its immunity. The function of the IgG is to act as a secondary response antibody.
IgM – These antibodies have μ- heavy chains in them. IgM has a valency of 5, which means that they are found in the form of pentamers only. Hence, it is the largest immunoglobulin molecule. IgM is the third most abundant human immunoglobulin found in the serum. It is expressed on the surface of the immature and mature B-cells as monomers. IgM is the first human immunoglobulin to be made by the foetus. The function of the IgM is to act as the primary response antibody.
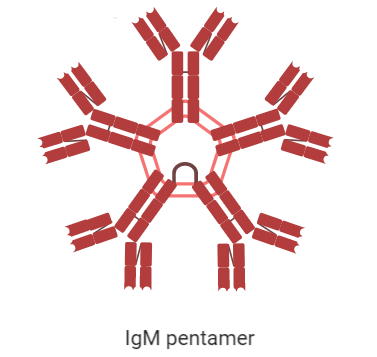
Note: The structure of the monomer of the antibody molecule is Y-shaped.
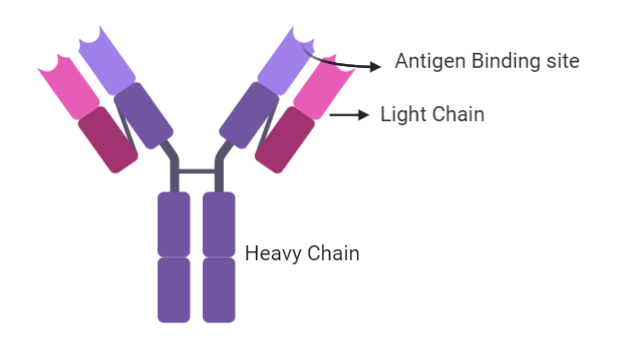
Every monomeric unit of an antibody molecule consists of 4 polypeptide chains. These are two light chains and two heavy chains. The light chains are usually the k or the λ chains. The heavy chains vary, and according to these various kinds of heavy chains the antibody molecule is classified. These chains are connected together by disulfide bonds. In antibodies, there is an antigen-binding site. The antigen-binding site in all the antibodies varies due to which they can adhere to only a specific kind of antigen. The antigen molecule that has the shape that can fit in the binding site can only attach with that antibody molecule. This makes all the antibodies antigen-specific.
