Question
Question: The four sets of shape and hybridization of xenon oxyfluorides are given. Choose the wrong set. A....
The four sets of shape and hybridization of xenon oxyfluorides are given. Choose the wrong set.
A. XeOF2−T−Shape−sp3d
B. XeOF4−Square pyramidal−sp3d2
C. XeO2F2−Distorted trigonal bipyramidal−sp3d
D. XeO3F2−Octahedral−sp3d
Solution
The geometry of any orbital can be concluded by the concept of hybridization. Where hybridization can be defined as the concept of mixing of two atomic orbitals with same energy levels and gives a new degenerated type of orbitals.
Complete answer:
When two atomic orbitals combine to form hybrid orbital in a molecule then redistribution of the energy of orbitals of individual atoms produces orbitals of equivalent energy and the new orbital forms are known as hybrid orbitals and the phenomenon is known as hybridization.
According to valence bond theory the metal atom or ion in presence of ligands can use its outer orbitals for hybridization which yield a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry like octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar and so on. These hybrid orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals which can easily donate electron pairs for bonding.
Given compound xenon oxyfluoride is represented by the chemical formula XeO3F2and the hybridization is discussed on the basis of lone pairs and bond pairs present in the compound, hence there is no lone pair present in XeO3F2and 5 bond pairs are there due to which it have sp3dhybridization. So, the compounds having sp3d hybridization will have trigonal bipyramidal shape not octahedral. The structure of XeO3F2 is given below:
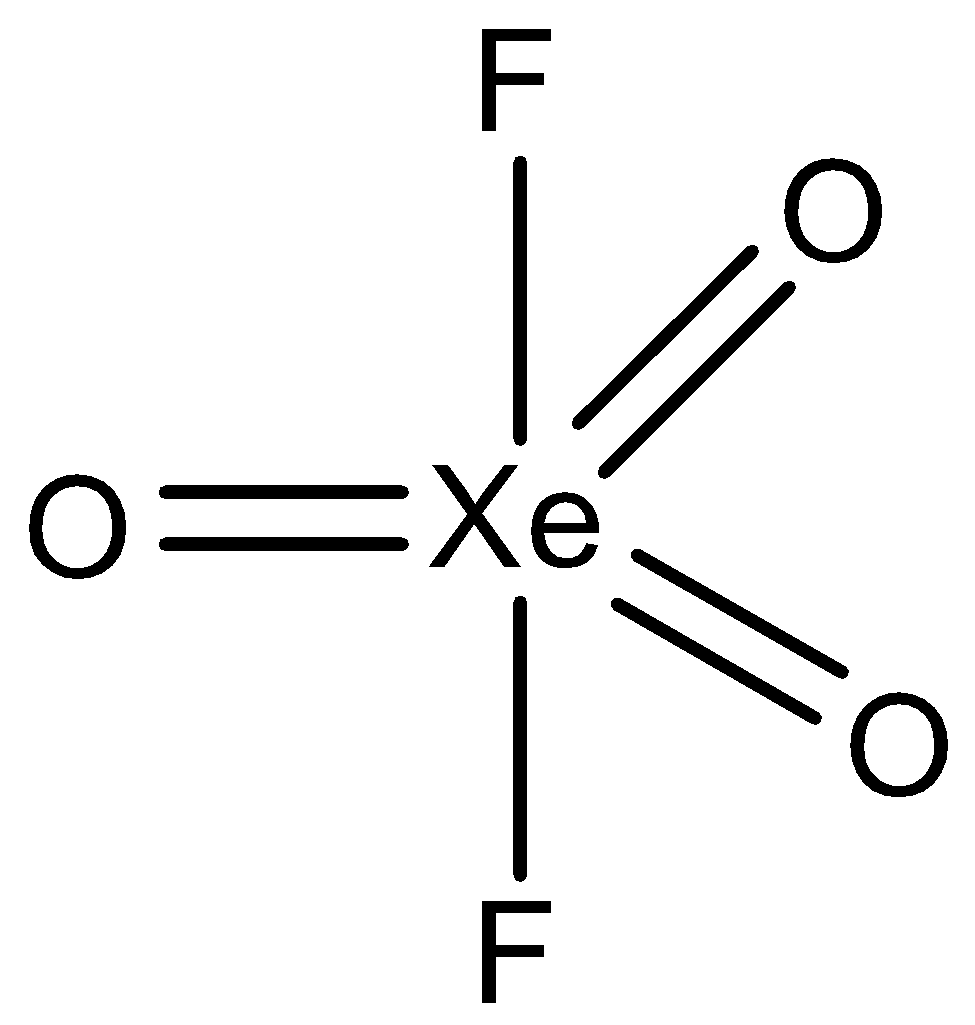
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
The shape and the hybridization of any compound can be concluded with the help of a theory given by the German Physicists called valence bond theory. This theory explains the electronic structure of the molecule formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals.
