Question
Question: The following two pedigrees describe the autosomal genetic disorders P and Q in Family 1 and Family ...
The following two pedigrees describe the autosomal genetic disorders P and Q in Family 1 and Family 2 respectively. Choose the correct statement from the following:
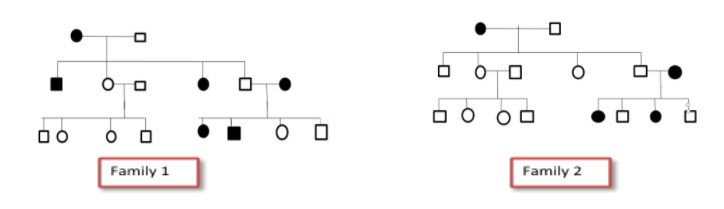
A. Both P and Q are dominant traits.
B. P is a dominant trait and Q is a recessive trait.
C. Both P and Q are recessive traits.
D. P is a recessive trait and Q is a dominant trait.
Solution
Pedigree analysis is used to identify if an offspring is likely to suffer from any genetic disorder by knowing the family history of the parental generation. If a trait is dominant it is likely to affect the next generation but if the trait is recessive it may either be inherited as a carrier or least number of offspring will be affected.
Complete answer:
If we study family 1, we see that male is unaffected by a disorder whereas the female has a genetic defect. The trait is transmitted to 1st, 4th and 6th child in 1st generation and then it gets transmitted to 5th and 6th child of the second generation. Since the mother carries the defective gene their offspring in second-generation are affected. Father has normal genes and hence the children who have normal genetic makeup are unaffected. The 2nd and 3rd are unaffected and hence their children are also unaffected but since 6th is affected (having defective genes) the resulting offspring are affected.
In case of family 2, if we consider the autosomal trait as dominant then the trait must be inherited to all the offspring of next-generation which is not the case in this pedigree and hence Q as a dominant trait can be struck off. If we consider the trait to be recessive then since the female is defective it must have two copies of a defective recessive gene and the male can be either homozygous dominant or heterozygous dominant (since it is normal). Since all the offspring of first-generation are normal therefore the female is homozygous recessive and the male should be homozygous dominant (if he is heterozygous dominant then 50% offspring must get affected, but resulting offspring of 1st generation are all normal). The resulting offspring of 1st generation are all carriers therefore one of the offspring pairs with a defected female 50% of children are affected.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: P is a dominant trait and Q is a recessive trait. For solving a pedigree, the genotypes are predicted logically by looking at the phenotypes and how a trait passes from one generation to next.
