Question
Question: The first step in photosynthesis is the (a) Formation of ATP (b) Absorption of light energy and...
The first step in photosynthesis is the
(a) Formation of ATP
(b) Absorption of light energy and loss of electrons from chlorophyll
(c) Splitting of water
(d) The reaction of CO2 with RuBP
Solution
Photosynthesis is an endothermic chemical process which helps in the formation of food in plants that is utilized by all organisms on earth to sustain.
Complete answer:
The first step of photosynthesis is the absorption of light energy and the loss of electrons from chlorophyll. Photosynthesis is a process by the plant to produce food by absorbing light of a certain wavelength and used to convert water and carbon dioxide and minerals into oxygen-rich and energy-rich organic compounds. The energy of the sunlight is a trap by the thylakoids which makes the electron excite and ultimately catalyze the hydrolysis of water.
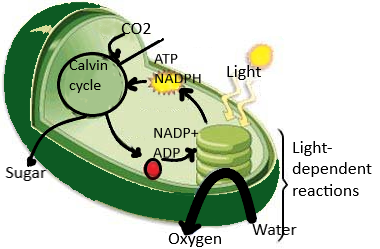
-In photosynthesis plant light is absorbed by the pigmented organic molecule called chlorophyll present in the chloroplasts.
-Chlorophyll has magnesium as the central metal ion and large organic molecule porphyrin contains four-four nitrogen atoms bound to the central metal ion.
-The chlorophyll absorbs light that causes an electron in the chlorophyll molecules is excited from a lower energy level to higher energy level and the excited electron is easily transferred to the other molecules and at the end hydrolysis water by removing an electron from water.
The major steps in the photosynthesis are-
-Absorption of light
-Electron transport
-Generation of ATP
-Carbon fixation
So, the correct answer is, ’absorption of light energy and loss of an electron from chlorophyll.’
Notes:
-Plants are the primary producers of the ecosystem and fuel to the next trophic levels.
-Not all plants are autotrophs, some are heterotrophs i.e. plants that cannot produce their food by carbon fixation they feed on other sources like small organisms.
-There are two stages of photosynthesis – light-dependent and light-independent reactions.
