Question
Question: The figure shows the motion of a planet around the Sun S in an elliptical orbit with the Sun at the ...
The figure shows the motion of a planet around the Sun S in an elliptical orbit with the Sun at the focus. The areas A and B can be assumed to be equal. If t1 and t2 represent the time taken for the planet to move from a to b, and c to d, respectively, then:
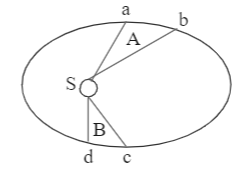
(A) t1<t2
(B) t1>t2
(C) t1=t2
(D) From the given information the relation between t1 and t2 cannot be determined.
Solution
Planetary motion in a fixed orbit is described using the Kepler’s Laws of Planetary motion. The time taken by a body to move a certain distance on the orbit depends upon its mass and the distance covered.
Complete step by step answer:
Planetary motion was a long-sought mystery in the history of humanity. From early ages, the ancient astronomers had tried to put forth various theories that would explain the motion of astronomical objects as was observed by the people on Earth.
It all started with the geocentric model, where the Earth was assumed to be the centre of the cosmos, and all the other objects including the Sun and stars revolved around it. The orbits were supposed to be perfectly circular, and the planets moved around the Earth in a uniform motion.
After many evolutions, the theory of planetary motion finally arrived at a heliocentric model, but still used circular orbits which did not fit well with the observed positions of stars.
It was only when Kepler gave his laws of motion, that the elliptical orbits for the orbits of planets were established and recognised. The second law of planetary motion by Kepler states that the areal velocity and hence, the angular momentum of a planet in motion around the Sun remains constant. This means for the same area (as given in the question), the areal velocity would be the same and hence the time taken by the planet to move from point a to b, and point c to d will also be the same.
Thus, the correct answer is option (C): t1=t2
Note:
The three scientific laws by Johannes Kepler were published between 1609 and 1619. Using the elliptical orbits specified by him, the retrograde motion of planets can be explained which remained a mystery for much of early astronomy.
