Question
Question: The figure shows the face and interface of a composite slab consisting of four lagers of two materia...
The figure shows the face and interface of a composite slab consisting of four lagers of two materials having identical thickness under steady state condition, find the value of temperature θ in 0C:
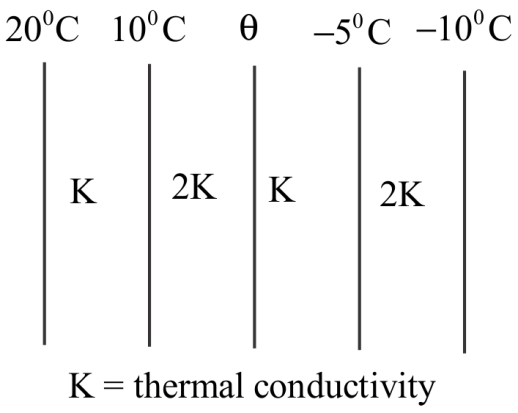
Solution
Under steady state, amount of heat dQ flows between the faces in time dt will be same for all faces i.e. the rate of flow of heat will be same in all the faces because all are in series combination. Series configuration in slabs defined by the same heat flow in the two conductors across all cross sections though they are different conductivity and temperature difference. On equating the rate of heat flow through slabs we can easily find out the required temperature.
Complete step by step solution:
According to question
The amount of heat dQ that flows between two faces in time dt is given by :
dtdQ=dKAΔt
Where
k→Thermal conductivity
A→Area of cross section of the face
ΔT→Difference in temperature of the faces
d→Thickness of the slab.
We know that the rate of flow of heat will be the same in all the faces because all are in series combination therefore in steady state the amount of heat dQ flows in the dt will be the same for all the faces.
(dtdQ)k=(dtdQ)2k
On putting the values we get
dKA(20−10)=d2KA(10−θ)
On simplification we get
(20−10)=2(10−θ)
10=20−2θ
∴2θ=10
On further solving we get
θ=5
Hence the value of temperature is 5∘C.
Note: The rate of heat flow is the amount of heat that is transferred per unit of time in some material, usually measured in watt. Heat is the flow of thermal energy driven by thermal non-equilibrium, so that 'heat flow' is a redundancy. If the slabs are placed in parallel then the rate of heat flow will be different.
