Question
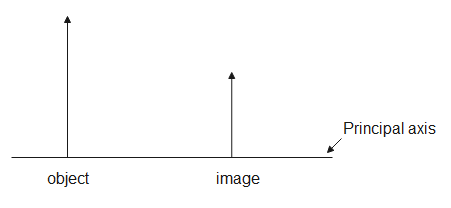
Question: The figure shows object \[O\] and diminished image \[I\]. This is possible if- (A). A convex mirro...
The figure shows object O and diminished image I. This is possible if-
(A). A convex mirror is placed to the right of I
(B). A convex mirror is placed between O and I
(C). A concave lens is placed to the right of I
(D). A concave lens is placed between O and I
Solution
A concave mirror forms virtual and diminished images by reflection behind the mirror, while a concave lens forms virtual and diminished images by refraction on the same side as the object. We can find the correct position where the image formed coincides with Iby observing the different positions of objects and corresponding image formations for the lens and mirrors.
Complete step-by-step solution
A convex mirror is curved outwards and forms a virtual diminished image, formed behind the lens for all positions of the object. According to sign convention, its focal length and radius of curvature, and image distance are taken as positive.
A concave lens is thinner in the center and thicker at the edges. It is called a diverging lens as the rays diverge after undergoing refraction. It forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image, formed on the same side of the lens as the object for all positions of the object. By convention, its focal length, the radius of curvature, and image distance are taken as negative.
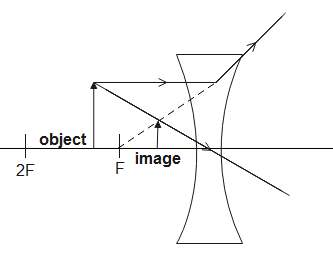
If we keep a concave lens in between O and I, the image formed, I′ by the lens will not coincide with I as I′ will be formed on the same side as O. If we keep the concave lens to the right of I, the image formed I′ may coincide with I
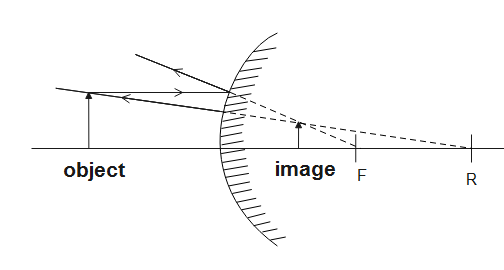
If we keep a convex mirror between O and I, the image formed,I′′ may coincide with I as the image formed by the convex lens on the other side of the mirror. Whereas if the mirror was to be kept on the right side of I, the image formed, I′′ would not coincide with I.
As the situation is possible if we keep a concave lens to the right of I or a convex mirror between O and I, the correct options are (B) and (C).
Note: By convention, all distances to the left are taken as negative and all distances to the right are taken as positive. A concave mirror forms real and inverted images for all positions except u<f. A convex lens always forms a real inverted image for all positions of an object except u<f.
