Question
Question: The figure shows an object and its image formed by a thin lens. Then the nature and the focal length...
The figure shows an object and its image formed by a thin lens. Then the nature and the focal length of the lens is
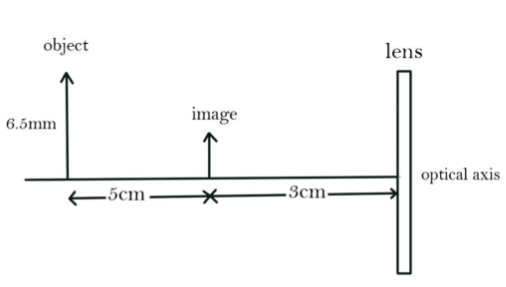
A) f=4.8cm converging lens
B) f=−4.8cm diverging lens
C) f=2.18cm converging lens
D) f=−2.18cm diverging lens
Solution
The object distance and image distance is given in the question. Just use the lens formula to find the unknown focal length of the lens. The lens formula is given as (f1)=(v1)−(u1)
Where f is the focal length of the lens, v is the distance of the image from the lens and u is the distance of the object from the lens.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The following information can be noted from the figure.
Object distance,u=−8cm
Image distance,v=−3cm
Using lens formula,
(f1)=(v1)−(u1)
f1=−31−−81
f=−4.8cm
We know that if the focal length is negative then the lens is diverging in nature. This is because the diverging rays are seen to intersect at the left side of the lens (which is against the direction of the incident ray when we measure it).
Option (B) is correct.
Additional information:
The concave lens or diverging lens is used in our daily life quite often. Some of the uses are as follows:
Glasses-Opticians use concave lenses to correct near-sightedness (also called myopia). A near-sighted eyeball is too long, and the image of a far-away object falls short of the retina. Concave lenses in glasses correct this shortfall by spreading out the light before it reaches the eye, thereby enabling the person using them to see distant objects more clearly.
Flashlights: Concave lenses are used on flashlights to magnify the light produced by the bulb. The light falls on the concave side of the lens, and the rays diverge on the other side, thereby increasing the apparent radius of the light source and providing a wider beam.
Lasers: Various types of medical equipment, scanners, and CD players use laser beams, and because these are highly focussed, they must often be dispersed in order for the equipment to work properly. Small concave lenses can widen a laser beam to precise access to a specific area. Concave lenses used with lasers are made from fused silica to withstand the ultraviolet rays produced by the light source.
Note:
According to the standard sign conventions, the sign of object distance and image distance are both negative in this case. This is because we always measure all the distance from the optical center of the lens. And if the direction of incident light is opposite of the direction of the measuring distance then the sign will be taken as negative which is exactly the case here.
