Question
Question: The figure represents three similar metal plates A, B, and C. They are placed parallel to each other...
The figure represents three similar metal plates A, B, and C. They are placed parallel to each other. Plate A is at a greater distance from B than C is from B. A source of fixed electro motive force is connected to the system such that B is connected to the positive terminal and A and C are connected to the negative terminal.
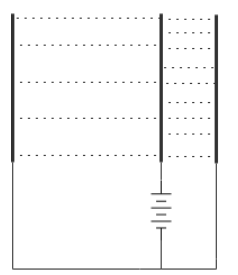
Identify the diagram which correctly indicates the iso lines of electric potential which has been given as dotted lines in the region between the plates?
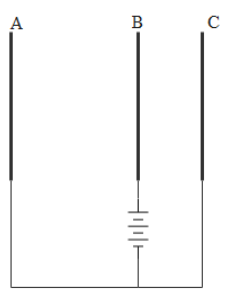
A.
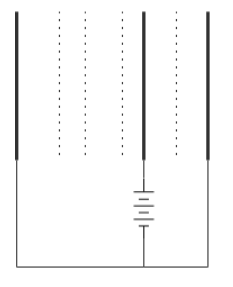
B.
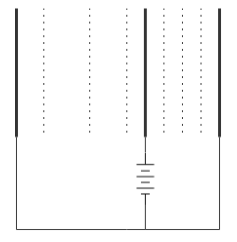
C.
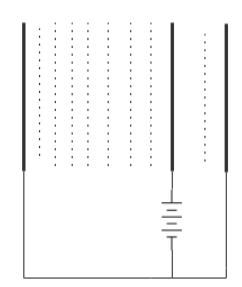
D.
Solution
First of all analyse the diagram well. We can see that the same battery has been placed in order to provide the potential difference. As the distance between the plates becomes higher, the electric field between the plates will become smaller. This all will help you in answering this question.
Complete answer:
As mentioned in the question, the same battery has been connected in between the two capacitors. Therefore the potential difference between both sets of plates will be similar to each other. As we look into the diagram, we can see that the distance between A and B is higher. Therefore the electric field between A and B will be smaller. This will produce a gradient between A and B which also must be smaller. Hence the equipotential surfaces must be denser between B and C than between A and B. this has been correctly shown in the diagram given as option.
Therefore the correct answer will be given as option B.
Note:
A capacitor is a device which is used in order to store the electric field. This energy is being stored between two metal plates which are separated by a distance containing a specific dielectric medium in between the metal plates. This device can operate only in the presence of alternate current. The unit of capacitor is given as Farad. A capacitor is defined as an electronic device and releases electricity in a circuit. It also generates alternating current without passing the direct current.
