Question
Question: The equations \[y = \pm \sqrt 3 x,{\text{ }}y = 1\] are the sides of (1) an equilateral triangle ...
The equations y=±3x, y=1 are the sides of
(1) an equilateral triangle
(2) a right- angled triangle
(3) an isosceles triangle
(4) a scalene triangle
Solution
To solve this question we will first find the coordinates of the triangle using given equations. After that we will find all the sides of the triangle using the Distance formula.
Formula Used:
d=(x2−x1)2+(y2−y1)2
Here, (x1,y1) is the first coordinate and (x2,y2) is the second coordinate. After finding all the sides, we will see that the given equation represents the sides of the triangle.
Complete answer: It is given that; the equations are
y=3x −−−(1)
y=−3x −−−(2)
y=1 −−−(3)
We will find out the coordinates of the triangle. Let the coordinates be A,B and C
First, we will find the coordinate A
So, on solving equation (1) and (2) we get
3x=−3x
(∵ as the left side of the equations are equal, so the right side will also be equal .)
⇒23x=0
⇒x=0
Now, if we put the value of x in any equation either (1) or (2) we get
⇒y=0
∴ the value of coordinate A will be (0,0)
Now, we will find the coordinate B
So, on solving equation (2) and (3) we get
−3x=1
⇒x=3−1
Now, if we put the value of x in equation (2) we get
⇒y=1
∴ the value of coordinate B will be (3−1,1)
Similarly, we will the coordinate C
So, on solving equation (1) and (3) we get
3x=1
⇒x=31
Now, if we put the value of x in equation (1) we get
⇒y=1
∴ the value of coordinate C will be (31,1)
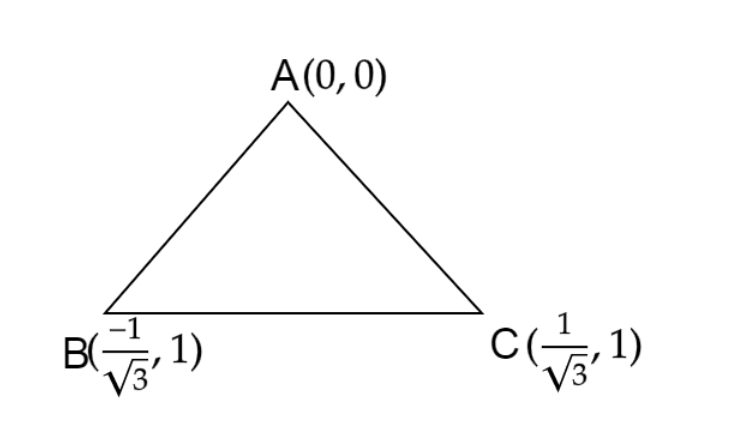
Now, we will find the sides of the triangle using Distance Formula, i.e.,
d=(x2−x1)2+(y2−y1)2
AB=(3−1−0)2+(1−0)2
⇒AB=(3−1)2+(1)2=31+1=34=32
Similarly,
BC=(31−(3−1))2+(1−1)2
⇒BC=(32)2=34=32
Similarly,
AC=(31−0)2+(1−0)2
⇒AC=(31)2+1=31+1=34=32
As we can see that all the sides are equal
⇒AB=BC=AC
Hence, it is an equilateral triangle.
Hence, option (1) is correct.
Note:
Before solving this question, one should know about the basic properties of all the triangles. Also, while calculating coordinates and distance, one should take care of the formula. And we can also solve the equation using the elimination method to calculate the coordinates but that creates difficulty and one can get stuck in the middle of the solution.
