Question
Question: The equation \[\left| {z + i} \right| - \left| {z - i} \right| = k\] represents a hyperbola if A....
The equation ∣z+i∣−∣z−i∣=k represents a hyperbola if
A.k∈(−2,2)
B.k∈(−2,0)
C.k \in \left\\{ {0,2} \right\\}
D.k \in \left\\{ { - 2,2} \right\\}
Solution
Here we need to find the range of the variable such that the equation will represent the equation of hyperbola. We will first assume the standard complex number and then we will substitute this value in the equation of the hyperbola. We will use the property of the hyperbola to find the range of the required variable.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given equation is
∣z+i∣−∣z−i∣=k ……………. (1)
Here we need to find the range of k such that this equation will represent the equation of hyperbola.
Let the complex number z be x+iy .
Now, we will substitute this value in equation 1.
⇒∣x+iy+i∣−∣x+iy−i∣=k
On simplifying the terms, we get
⇒∣x+i(y+1)∣−∣x+i(y−1)∣=k
We know that ∣a+ib∣=a2+b2
Using this property of complex number, we get
⇒x2+(y+1)2−x2+(y−1)2=k
On further simplification, we get
⇒x2+(y+1)2=k−x2+(y−1)2
On squaring both sides, we get
⇒(x2+(y+1)2)2=(k−x2+(y−1)2)2
We know from the algebraic identities that (a−b)2=a2+b2−2ab
Using this identity here, we get
⇒x2+(y+1)2+2×x×(y+1)=k2+(x2+(y−1)2)2−2×k×x2+(y−1)2
On further simplification, we get
⇒x2+(y+1)2=k2+x2+(y−1)2−2×k×x2+(y−1)2
Now, again we will use the algebraic identities:-
(a−b)2=a2+b2−2ab
(a+b)2=a2+b2+2ab
⇒x2+y2+2y+1=k2+x2+y2−2y+1−2×k×x2+y2−2y+1
We will add and subtract the like terms on both sides
⇒2×k×x2+y2−2y+1=k2−4y
On squaring both sides, we get
⇒(2×k×x2+y2−2y+1)2=(k2−4y)2 ⇒4k2(x2+y2−2y+1)=(k2−4y)2
Now, we will use the the algebraic identity :-
(a−b)2=a2+b2−2ab
Using this identity, we get
⇒4k2(x2+y2−2y+1)=k4+16y2−8yk2
On multiplying the terms, we get
⇒4k2x2+4k2y2−8k2y+4k2=k4+16y2−8yk2
Now, we will add and subtract the like terms, we get
⇒4k2x2+(4k2−16)y2−k4+4k2=0…………… (2)
We know the general equation is given by
⇒ax2+by2+2hxy+2gx+2fy+c=0 …………. (3)
We know that this general equation will represent the equation of hyperbola when h2−ab>0
Now, we will compare equation 2 and equation 3 i.e. we will compare the obtained equation with the general equation.
a=4k2\b=4k2−16\h=0\g=0=¸−k4+4k2
The obtained equation will represent the equation of hyperbola when h2−ab>0
Substituting h=0,a=4k2 and b=4k2−16 in the above equation, we get
02−(4k2)(4k2−16)>0
On further simplification, we get
⇒−4k2(4k2−16)>0
Multiplying −1 to both sides of inequality
⇒4k2(4k2−16)<0
We can write this inequality as
⇒16k2(k−2)(k+2)<0
Now, we will number lines to solve this inequality.
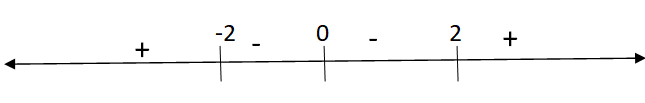
We can see from the number line that k∈(−2,2) is satisfying the inequality.
Hence, the k∈(−2,2) is the required answer.
Therefore, the correct option is option A.
Note: To solve this question, we need to know the basic properties of the hyperbola and how a general equation is used for different equations. Here we have also solved the inequality to get the required value. When we divide or multiply a negative number on both sides of the inequality, the sign of inequality gets changed but when we add or subtract the number on both sides of the inequality, the sign of inequality remains unchanged.
