Question
Question: The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is \(-119.5 kJ mol^{-1}\). If resonance energy of benze...
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is −119.5kJmol−1. If resonance energy of benzene is −150.4kJmol−1, its enthalpy of hydrogenation would be:
A. −269.9kJmol−1
B. −358.5kJmol−1
C. −508.9kJmol−1
D. −208.1kJmol−1
Solution
Hint: There are 3 double bonds in benzene and for breaking 3 double bonds, 3 H2 molecules are required. We should remove resonance energy from total enthalpy of the reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
This is the hydrogenation reaction of cyclohexene:
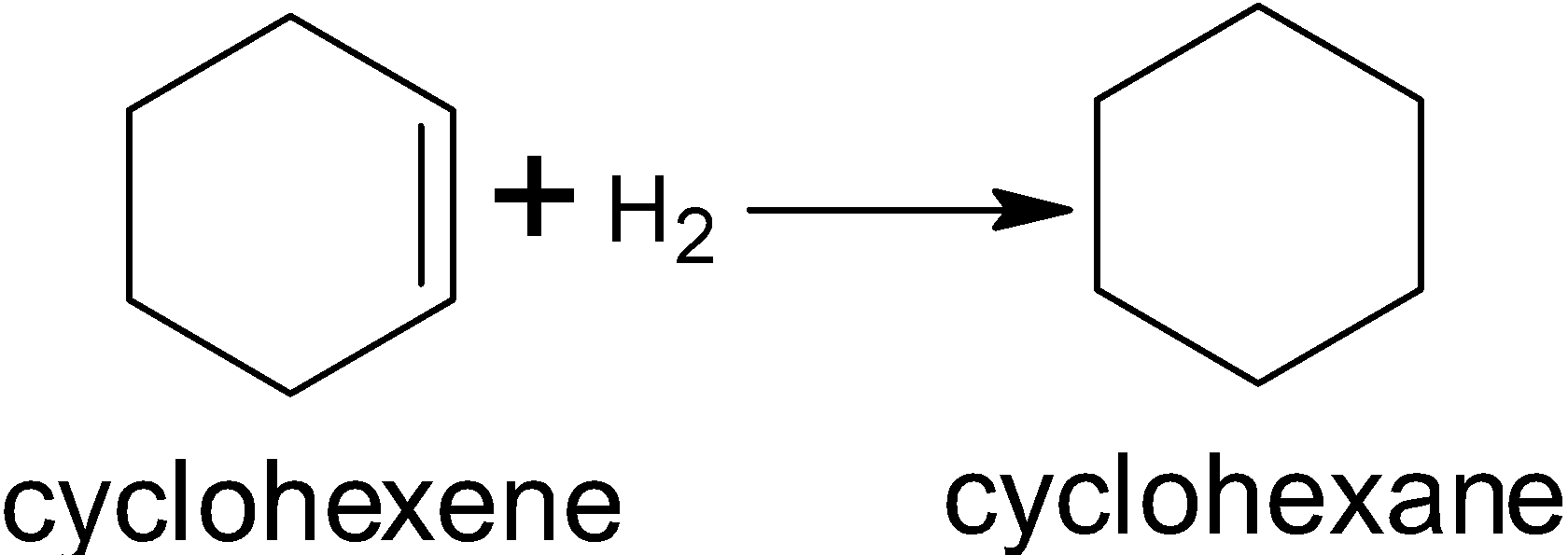
In this reaction for breaking one double bond one hydrogen molecule is required and in benzene 3 double bonds are there so 3 hydrogen molecules are required for breaking double bonds of benzene.
Given, Enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene(ΔHcyclohexene) = −119.5kJmol−1
Here, Enthalpy of benzene (ΔHbenzene) = 3 x (enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene)
= 3 x (−119.5kJmol−1)
= −358.5kJmol−1
Given, resonance energy of benzene = −150.4kJmol−1
So, for calculating actual enthalpy of hydrogenation = Enthalpy of benzene – resonance energy of benzene.
From given data:
Enthalpy of hydrogenation = (-358.5) - (-150.4)
= −208.1kJmol−1
So, the answer is “D”.
Note: Don’t forget to take signs of energy or enthalpy in calculation. You should remove resonance energy from the total enthalpy of reaction. For breaking every π bond 1 molecule of hydrogen is required.
