Question
Question: The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is \( - 119.5{\text{ kJ mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}\). If r...
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is −119.5 kJ mol−1. If resonance energy of benzene is −150.4 kJ mol−1, its enthalpy of hydrogenation would be
A) −508.9 kJ mol−1
B) −208.1 kJ mol−1
C) −269.9 kJ mol−1
D) −358.5 kJ mol−1
Solution
We know that benzene (C6H6(l)) contains three double bonds. To break these three bonds and convert benzene (C6H6(l)) to cyclohexane (C6H12(l)) three molecules of hydrogen (H2) will be required. To calculate the enthalpy of hydrogenation of the given compound we must add resonance energy to the total enthalpy of the reaction.
Complete solution:
We are given that the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is −119.5 kJ mol−1. The enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is the enthalpy for addition of one molecule of hydrogen to cyclohexane.
The enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is the enthalpy for addition of one molecule of hydrogen to cyclohexane. The hydrogenation reaction of benzene is as follows:
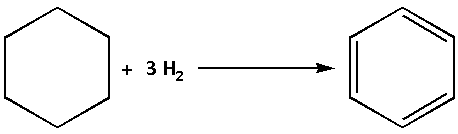
We are given that the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene is −119.5 kJ mol−1. Thus, the enthalpy for hydrogenation of benzene is,
ΔHbenzene=3×ΔHcyclohexene
Where ΔHcyclohexene is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexene,
ΔHbenzene is the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene.
ΔHbenzene=3×−119.5 kJ mol−1
ΔHbenzene=−358.5 kJ mol−1
Thus, the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is −358.5 kJ mol−1.
We know that benzene is a resonating structure. Thus, benzene possesses resonance energy. The amount of energy required to convert the true delocalized structure into stable structure is known as resonating energy. Thus,
Resonance energy=ΔHbenzene−ΔHbenzene (actual)
We are given that the resonance energy of benzene is −150.4 kJ mol−1. Thus,
−150.4 kJ mol−1=−358.5 kJ mol−1−ΔHbenzene (actual)
−ΔHbenzene (actual)=−150.4 kJ mol−1+358.5 kJ mol−1
−ΔHbenzene (actual)=208.1 kJ mol−1
ΔHbenzene (actual)=−208.1 kJ mol−1
Thus, the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is −208.1 kJ mol−1.
Thus, the correct option is (C) 8.87.
Note: The amount of energy required to convert the true delocalized structure into stable structure is known as resonating energy. The resonance energy is the measure of extra stability of a conjugated system compared to the number of isolated double bonds.
