Question
Question: The energy-releasing metabolic process in which substrate is oxidized without an external electron a...
The energy-releasing metabolic process in which substrate is oxidized without an external electron acceptor is called as-
(a)Photorespiration
(b)Glycolysis
(c)Fermentation
(d)Aerobic respiration
Solution
It is a metabolic process that, through the action of enzymes, induces chemical changes in organic substrates. It is broadly described in biochemistry as the extraction of carbohydrate energy in the absence of oxygen.
Complete answer:
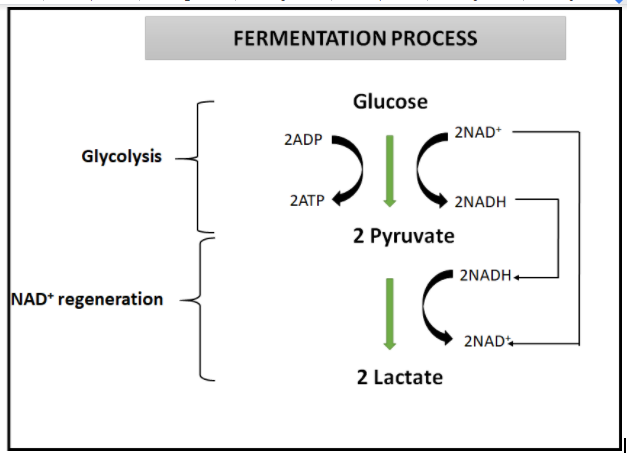
In the absence of oxygen (external electron acceptor), fermentation is incomplete oxidation of food substances into alcohol or lactic acid, with a small amount of energy being released. As an electron acceptor for the oxidation of substrates, aerobic respiration requires oxygen. The first common stage of both fermentation and aerobic respiration is glycolysis.
Photorespiration is the oxidation of RuBP by the RUBISCO enzyme and does not generate energy. In microorganisms, the primary means of producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by anaerobic degradation of organic nutrients is fermentation. Since the Neolithic era, people have used fermentation to produce foodstuffs and beverages. For example, in a process that produces lactic acid contained in sour foods such as pickled cucumbers, kombucha, kimchi, and yogurt, fermentation is used for preservation, as well as to produce alcoholic drinks such as wine and beer. Within the gastrointestinal tracts of all species, including humans, fermentation often takes place.
Additional Information: Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy into adenosine triphosphate from oxygen molecules or nutrients and then to release waste products.
The mechanism by which one glucose molecule is converted into two pyruvate molecules, two hydrogen ions, and two water molecules is glycolysis. The 'high-energy' molecules of ATP and NADH are synthesized via this process. The molecules of pyruvate then proceed to the link reaction, where acetyl-CoA is produced.
Photorespiration refers to a phase in plant metabolism where the enzyme RuBisCO oxygenates RuBP, wasting some of the energy provided by photosynthesis (also known as the oxidative photosynthetic carbon cycle, or C2 photosynthesis).
So, the correct answer is ‘fermentation’.
Note: The action of yeast on fermentable sugars to produce carbon dioxide (CO2), ethanol, and some aromatic compounds is the main method of fermentation. Organoleptic characteristics of bread depending on the conditions of fermentation of the dough, namely the texture, taste, and aroma.