Question
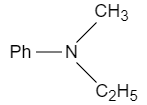
Question: The end product \((2)\) of the reaction sequence:  of the reaction sequence:
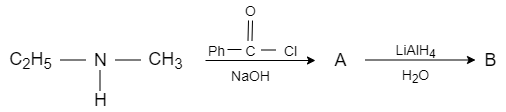
A.
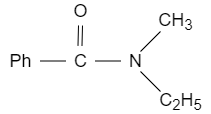
B.
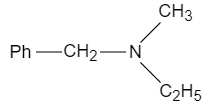
C.
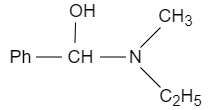
D.
Solution
In this question, Heinsberg test is used to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary amines. In this test, amine is reacted with benzene carbonyl chloride.
LiAlH4 acts as a strong reducing agent .
Complete step by step answer:
Lithium aluminium hydride is an inorganic compound having formula, LiAlH4 . It acts as a strong reducing agent which is used for the reduction of amides, esters, carboxylic acids to alcohols and ketones. It also reduces alkyl halides to alkane.
Benzene carbonyl chloride having the formula C6H5CPOCl is a colorless fuming liquid. It is an organochlorine compound which is mainly used for the production of peroxides. It is used for the preparation of dyes, perfumes and raisins.
When ethyl methyl amine is reacted with benzene carbonyl chloride in presence of sodium hydroxide, the benzoyl radical from benzene carbonyl chloride attacks on acidic hydrogen and forms benzoyl ethyl methyl amide, which reacts with lithium aluminium hydride that acts as a reducing agent and converts it into N− ethyl −N− methyl −1− hydroxy −1− phenylmethanamine. It converts the carbonyl carbon into alcohol.
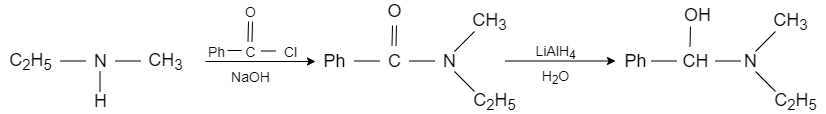
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Additional information:
We can prepare benzoyl chloride from benzo trichloride with water or benzoic acid.
Lithium aluminum hydride is a colorless solid, but due to contamination, their commercial samples are grey. Lithium aluminium hydride can be purified by recrystallisation from diethyl ether. It reacts violently with water.
LiAlH4+4H2O→LiOH+Al(OH)3+4H2
This reaction can be used for the production of hydrogen in the laboratory.
Note: In conclusion, the ethyl methyl amine reacted with benzene carbonyl chloride with sodium hydroxide and a strong reducing agent with water, it results in the formation of N− ethyl −N− methyl −1− hydroxy −1− phenylmethanamine.
