Question
Question: The emf of the battery shown in the figure is 
(A) 12V
(B) 16V
(C) 18V
(D) 15V
Solution
Hint : In the electrical circuit given in the above question we need to find E in volts. We will use resistance simplification and Kirchhoff’s Voltage and Current Laws. We will use V=IR , where V is the voltage drop across a resistor along the direction of current flow, R is the resistance to be used from the diagram given, and I is the current through the specific resistance.
Formula Used: Voltage = Current×Resistance
Complete step by step answer
Let us assume the notation Vxy to denote the voltage drop between two points, say Vx and Vy .
We redraw the diagram adding the two resistances in series in the right-most branch. The formula for a series combination of resistances is
⇒Rnet=R1+R2+...
Here Rnet=2Ω+1Ω=3Ω as shown in the figure.
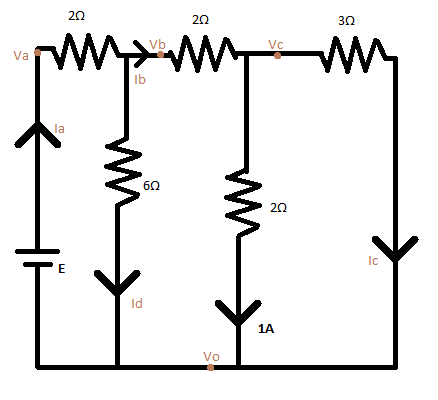
Using V=IR across the 2Ω resistor through which 1A current is flowing, we get
⇒Vco=1A×2Ω=2V
∴Ic=3ΩVco=3Ω2V=32A
Applying Kirchhoff’s Circuit Law again we get
⇒Ib=1A+Ic=1A+32A=35A
Now to get Vbc , we use V=IR across the resistor through which current Ib is flowing.
⇒Vbc=Ib×2Ω=35A×2Ω=310V .
∴Vbo=Vbc+Vco=310V+2V=316V
Now we can calculate Id as,
⇒Id=6ΩVbo=6Ω316V=98A
Applying Kirchhoff’s Circuit Law again we get
⇒Ia=Ib+Id
⇒Ia=35A+98A=923A
Applying V=IR across the resistor through which current Ia is flowing, we get
⇒Vab=Ia×2Ω=923A×2Ω=946V
Therefore we can say that,
⇒Vao=Vab+Vbo
⇒Vao=946V+316V=994V
From the diagram, we see that the voltage drop across the battery is the same as the voltage drop between Va and Vo . Thus, since E=Vao , the emf of the battery is E=994V=10.444V≈12V . We approximate the voltage since it is the closest option as given in the question. Also, the voltage drop across the battery will be less than the emf of the battery due to the internal resistance of a battery. Thus the emf is equal to the voltage drop only in the ideal case.
The correct option is (A) 12V .
Note
We can also calculate E=Vao by applying Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law along the path a−b−c−o−a . This way we will get the same result. The other ways of calculating E from the same figure using different paths are a−b−o−a and a−b−c−o−a . In each of these processes, we will require the current in each of the resistors involved in the circuit and so we have chosen the above process.
