Question
Question: The electric field due to an electric dipole at a distance r from its center in axial position is E....
The electric field due to an electric dipole at a distance r from its center in axial position is E. If the dipole is rotated through an angle of 90∘ about its perpendicular axis, the electric field at the same point will be
(a). E
(b). 4E
(c). 2E
(d). 2E
Solution
- Hint: First let us learn about electric dipole and the net field created due to the dipole. An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative charges in an electromagnetic system. A pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite signs separated by some small distance is an example for electric dipole.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We know that an electric charge produces an electric field around it. This electric field magnitude decreases with increase in distance from the charge producing that field. Hence, we can say that more the distance from the charged particle, less the magnitude of the electric field. The electric field at a point due to a charge is given by:
E=r2kq , where E is the electrical field at the point, q is the charge, and r is the distance between the points.
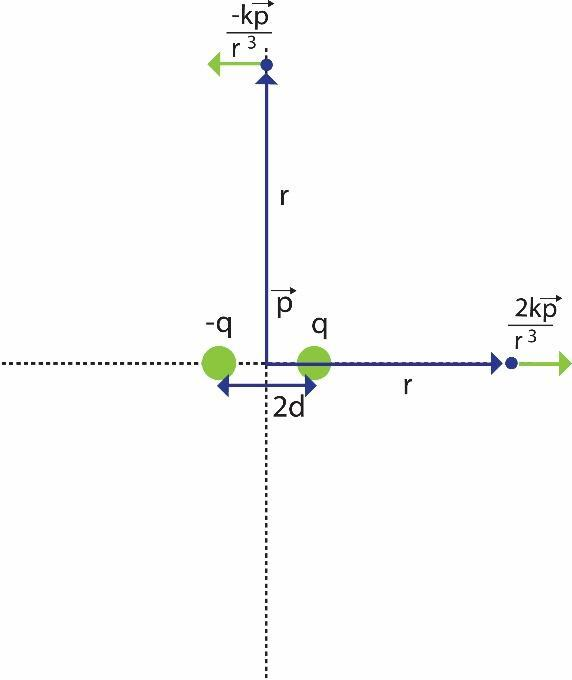
Two charges with equal magnitude and opposite charge separated by a distance is known as Electric dipole. The distance between the two oppositely charged particles is extremely small (assumed to be 2d) that both the electric fields produced will combine to produce net electric field. The center of the electric dipole is defined as the midpoint of the imaginary line between the two opposite charges. The axis of the dipole is the line joining both the charges. Refer to the figure.
The electric field due to an electric dipole at a distance r from its center in axial position is,
