Question
Question: The effective resistance between the points \(A\) and \(B\) in the circuit shown in Fig. will be: ...
The effective resistance between the points A and B in the circuit shown in Fig. will be:
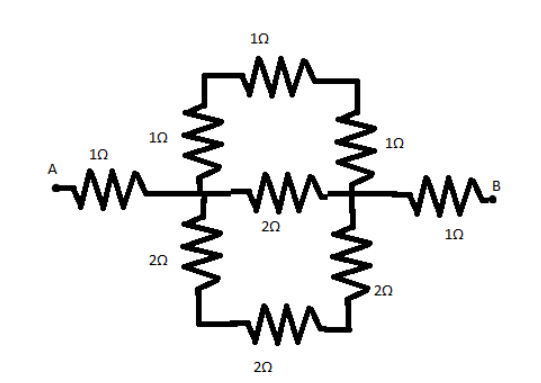
(A) 6Ω
(B) 3Ω
(C) 15Ω
(D) 10Ω
Solution
We will use the general formula of adding resistances here. The net resistance between points A and B is the same as the addition of net resistances between points A and C, C and D, D and B which is given in the below figure. We will simplify the resistances using the formulas below.
Formula used: Resistance calculation in series Rseries=R1+R2+...
Resistance calculation in parallel Rparallel1=R11+R21+...
Complete Step by step solution:
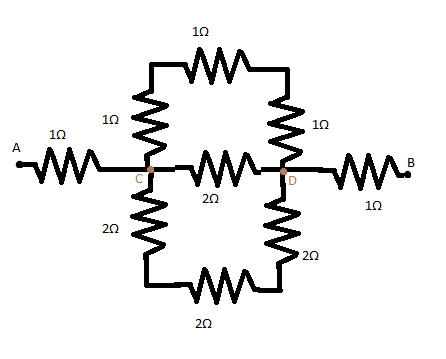
In the given diagram,
Net resistance between A and B is calculated by adding the net resistances between A and C, C and D, D and B since they will be in series.
Therefore, RAC=1Ω as can be seen, from the figure.
In the calculation of RCD, we see that the three 1Ω resistances are in series. We use the series resistance formula here to get the net resistance as 1Ω+1Ω+1Ω=3Ω on the top branch.
Similarly, the three 2Ω resistances are also in series. We use the series resistance formula again to get the net resistance as 2Ω+2Ω+2Ω=6Ω on the bottom branch.
These 3Ω net resistance of the top branch, 2Ω resistance of the middle branch, and 6Ω net resistance of the bottom branch are now in parallel.
Hence, we use the formula for resistances in parallel to get the net resistance as Rparallel1=3Ω1+2Ω1+6Ω1
⇒Rparallel1=6Ω2+3+1=1Ω1
∴Rparallel=1Ω
This is the net resistance between points C and D. Thus RCD=1Ω.
The resistance between points D and B, i.e. RDB=1Ω as can be seen from the figure given.
Now the resistances RAC, RCD and RDB are in series.
We will therefore use the series formula for summation of resistances.
Rnet=RAC+RCD+RDB=1Ω+1Ω+1Ω=3Ω
⇒Rnet=3Ω
Thus the net resistance between the points A and B is equal to 3Ω.
Therefore option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: The other process of calculating the equivalent or net resistance between two points includes assuming a current of 1A flowing through the circuit and calculating the net voltage drops from a specific point. After finding the net voltage drop, we will use the formula V=IR, to find the R, i.e. effective resistance in case of complicated circuits.
