Question
Question: The ease of dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halide with alcoholic KOH is: A. \({{\text{3}}^{\text{o}}...
The ease of dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halide with alcoholic KOH is:
A. 3o<2o<1o
B. 3o>2o>1o
C. 3o<2o>1o
D. 3o>2o<1o
Solution
Hint : This type of reactions results in elimination of certain atoms of the haloalkane and thus follows the mechanism and forms an alkene.This is a single step process, and has no transition states of carbocations and carbanions.
Complete step by step solution :
Now first let us understand the dehydrohalogenation reaction:
-So, as the name suggests when the leaving group is a halogen atom with also the elimination of a water molecule,we call the reaction as dehydrohalogenation.
-This reaction results in formation of alkenes.
-This process is also known as beta- elimination reaction,as we eliminate !!β!! - hydrogen from the haloalkane.
-We should also know that the !!β!! -carbon atom is the next atom beside the carbon which has halogen attached to it.
- When an alkyl halide is boiled with a concentrated alcoholic potassium hydroxide, they undergo !!β!! - elimination reaction.In this reaction the hydrogen atom of haloalkane is eliminated which comes from a !!β!! -carbon( !!β!! -carbon is the carbon that comes next to the halogen atom).
- And as the hydrogen atom is eliminated, to form a water molecule,the halogen atom which is attached to alpha carbon leaves the group and the alkyl group now forms an alkene.
-The following reaction will explain the elimination reaction:
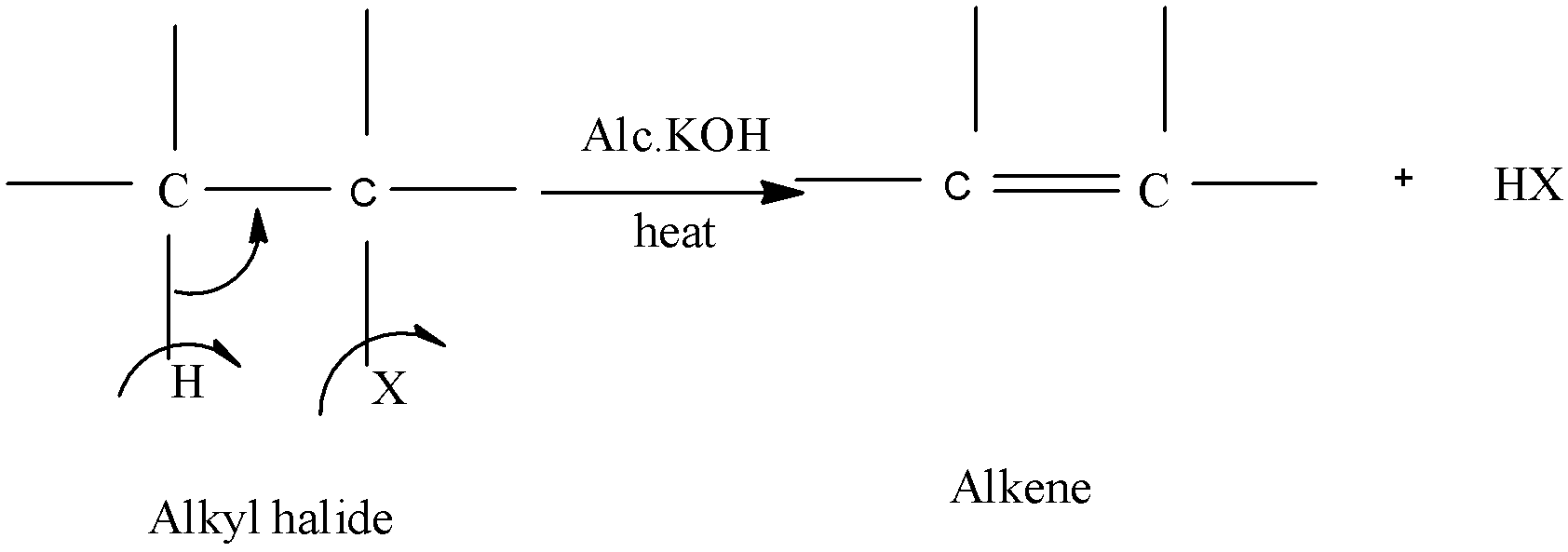
- Now in order to understand the reactivity order of alkyl groups towards dehydrohalogenation is due to a rule known as Satyzeff's rule.
- This rule states that when any alkyl halide which will give a more stable or the most highly substituted alkene must undergo dehydrohalogenation faster then the one which will be relatively less stable.
- Thus the reactivity order is given by:
- 3o>2o>1o
- And the right option is B.
Note : So ,as we use here the alcoholic KOH ,the reason here for using it is that the hydroxide ion is a very strong base,and thus it pulls off a hydrogen atom in order to form a water molecule,and thus resulting in the formation of carbon - carbon double bond.We must also remember that high temperature and concentration favours elimination reaction
