Question
Question: The domain of the function \(y = \sqrt {\sin x + \cos x} + \sqrt {7x - {x^2} - 6} \) is \(\left[ {p,...
The domain of the function y=sinx+cosx+7x−x2−6 is [p,4qπ]∪[4rπ,s], then the value of p + q + r + s is
Solution
Hint – In this question first use the concept that the domain of square root is greater than equal to 0, thus sinx+cosx⩾0 and 7x−x2−6⩾0. For the terms involving trigonometric ratios convert them into the form sin(A+B) by multiplying and dividing sinx+cosx⩾0 by 2 . Solving the inequality will help to get the answer.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given equation
y=sinx+cosx+7x−x2−6
Now to find out the domain the function which is in square root is always greater than or equal to zero.
⇒sinx+cosx⩾0 ............. (1) and 7x−x2−6⩾0........................... (2)
Now first solve first equation we have,
⇒sinx+cosx⩾0
Now multiply and divide by 2 we have,
⇒2(21×sinx+21×cosx)⩾0
Now as we know that sin450=cos450=21
⇒2(cos45×sinx+sin45×cosx)⩾0
⇒(cos450×sinx+sin450×cosx)⩾0
Now as we know that sin(A+B)=sinAcosB+cosAsinB so use this property in above equation we have,
⇒sin(x+4π)⩾0, [∵450=4π]
Now as we know sinx⩾0, x∈[0,π],[2π,3π],....
⇒0⩽(x+4π)⩽π and 2π⩽(x+4π)⩽3π .................
⇒−4π⩽x⩽π−4π and 2π−4π⩽x⩽3π−4π .................
⇒−4π⩽x⩽43π and 47π⩽x⩽411π
⇒x∈[−4π,43π],[47π,411π]................. (3)
Now consider equation (2) we have,
⇒7x−x2−6⩾0
Now multiply by (-1) so the inequality sign reversed so we have,
⇒−7x+x2+6⩽0
⇒x2−7x+6⩽0
Now factorize this equation we have,
⇒x2−x−6x+6⩽0
⇒x(x−1)−6(x−1)⩽0
⇒(x−1)(x−6)⩽0
⇒x∈[1,6]............................. (4)
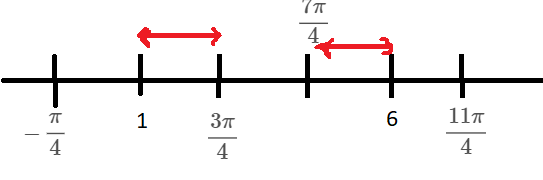
So the domain of the given equation is the intersection region of equation (3) and (4).
Now 4−π<1, 43π>1, 47π<6, 411π>6
Now the common region is shown in the above diagram so the domain of the given function is
⇒[1,43π]∪[47π,6]
So on comparing with [p,4qπ]∪[4rπ,s]
⇒p=1,q=3,r=7,s=6
So the value of p + q + r + s is
⇒p+q+r+s=1+3+7+6=17
So this is the required answer.
Note – The domain of a function corresponds to the possible values of the independent variable that is x in this case, for which the entire function is defined. For example the domain of a quadratic function like ax2+bx+c=0 is x∈R as this quadratic is defined for any value of x belonging to real axis from−∞ to +∞.
