Question
Question: The distance between earth and moon is about \(3.8 \times {10^5}\,km\) . At what point(s) will the n...
The distance between earth and moon is about 3.8×105km . At what point(s) will the net gravitational force of the earth-moon system be zero? (Given mass of earth is 81 times the moon’s mass)
A) 38×109m
B) 38×107m
C) 8×107m
D) 3.8×107m
Solution
The net gravitational force of the earth-moon system will be zero when the gravitational force of the earth will be balanced by that of the moon. This means that the gravitational potential of the earth will be equal to that of the moon for this particular point.
Formula Used:
Gravitational force on a body of mass m due to another body of mass M separated by a distance r is given by r2GMm where, G is the universal gravitational constant with value 6.67×10−11Nm2kg−2
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Consider a point P between Earth and Moon at a distance of r kilometres from the Earth. Let the distance between Earth and Moon be R . Therefore, R=3.8×105km (given in question)
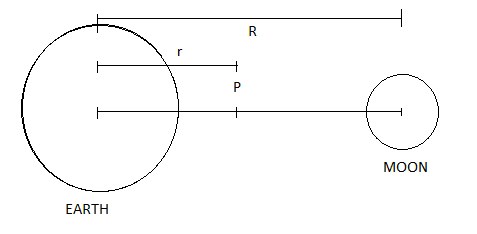
Let the mass of Earth be M and mass of moon be m and the mass of object P be m′
Therefore, M=81m (given in question)
Gravitational force on object P due to Earth =r2GMm′=r2G×81m×m′ (because of above equation)
Gravitational force on object P due to Moon =(R−r)2Gmm′=[(3.8×105)−r]2Gmm′
Now, the net gravitational force experienced by the object P at a distance r kilometres from the Earth must be zero. So, the force on it due to the Moon and the Earth must be equal.
Therefore, r2G×81m×m′=[(3.8×105)−r]2G×m×m′
After cancelling out similar variables, we are left with
r281=[(3.8×105)−r]21
Take the square root of the entire equation. We get
r9=(3.8×105)−r1
⇒9[(3.8×105)−r]=r
⇒9(3.8×105)−9r=r
On simplifying, we get 10r=9(3.8×105)
Or, r=3.42×105km=34.2×107m
We see that this answer is not given in any of the options so the answer closest to it will be the correct answer to the question (taking in account the physical errors while calculation)
Hence, option B is the correct answer.
Note: Do not confuse G with g . The first one is the universal gravitational constant. Its value is the same throughout the universe. Its value is 6.67×10−11Nm2kg−2 . The latter is acceleration due to gravity. Its value on earth is 9.8ms−2
