Question
Question: The diagram shows a uniformly charged hemisphere of radius \(R\). It has volume charge density \(ρ\)...
The diagram shows a uniformly charged hemisphere of radius R. It has volume charge density ρ. If the electric field at a point 2R distance above its center is E then what is the electric field at the point which is 2R below its center?
A. 6εoρR+E
B. 12εoρR−E
C. −6εoρR+E
D. 24εoρR+E
Solution
The electric force per unit charge is known as the electric field. The force that the field will apply on a positive test charge is assumed to be in the same direction as the field's direction. A positive charge's electric field is radially outward, and a negative charge's field is radially inward.
Complete step by step answer:
Permittivity is a proportionality constant that connects the electric field in a substance to its electric displacement. It describes the tendency of an insulating material's atomic charge to deform in the presence of an electric field. Gauss' law can be used to calculate the electric field of a sphere with uniform charge density and cumulative charge Q. The electric field has the same magnitude at any point of a Gaussian surface in the shape of a sphere with radius r>R and is directed outward.
E=4πε0r2Q
Let's finish the sphere. The electric field produced by the lower part at A is equal to the electric field generated by the upper part at B=E. (given) At B, the electric field due to the lower part equals the electric field due to the entire sphere minus the electric field due to the upper part.
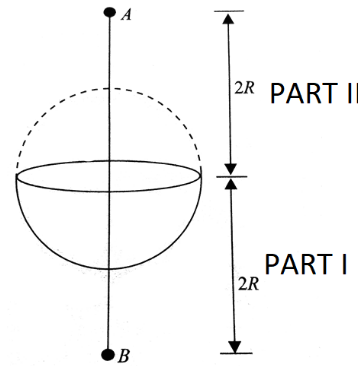
Net field due to part I and II at A=(2R)2NQ
⇒ Net field due to part I and II at A=(2R)2kQ−E ⇒ Net field due to part I and II at A=4πε014R2ρ(4/3πR3)−E ∴ Net field due to part I and II at A=12ε0ρR−E
Hence option B is correct.
Note: The energy contained in an electric field is linked to the electric permittivity. Since it concerns the amount of charge that must be levied on a capacitor to obtain a certain net electric field, it is used in the capacitance phrase. It takes more charge to obtain a given net electric field in the presence of a polarizable medium, and the effect of the medium is often expressed in terms of relative permittivity.
