Question
Question: The diagram given represents a certain stage of mitosis: (i) Identify the stage of cell division. ...
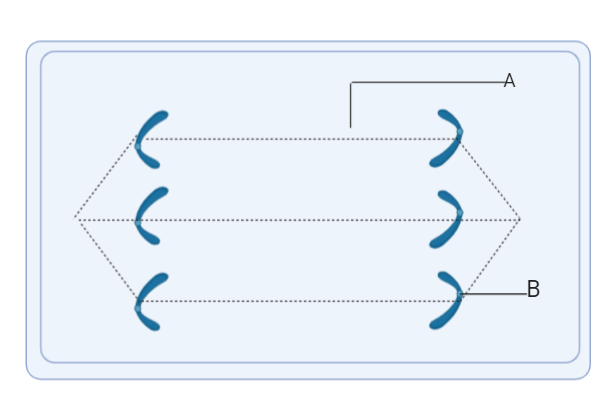
The diagram given represents a certain stage of mitosis:
(i) Identify the stage of cell division.
(ii) Name the parts labelled A and B.
(iii) What is the unique feature observed in this stage?
(iv) How many daughter cells formed from this type of cell division?
Solution
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle of cell biology, where replicated chromosomes are divided into two new nuclei. Mitosis produces genetically similar cells that retain the total chromosome count.
Complete answer:
(i)The cell is seen as the chromatid sister shifts towards the opposite poles in anaphase. Anaphase, when replicated chromosomes are separated and the newly-copied chromosomes are transferred to opposite poles of the cell, is the stage of mitosis after the metaphase process. The splitting of the sister chromatids marks the beginning of anaphase. These sister chromatids become the nuclei of the daughter chromosomes. The chromosomes are then pulled by the fibres attached to each chromosome's kinetochores towards the pole. Each chromosome's centromere leads to the edge as its arms trace.
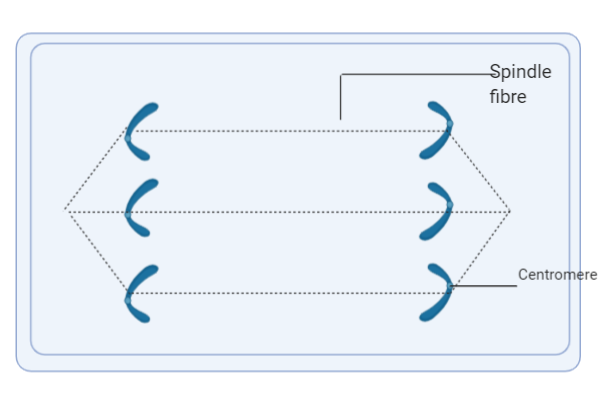
(ii) A-Spindle fibre, B-centromere. Fibres of the spindle are filaments which form the mitotic spindle, i.e., mitosis and meiosis. They are primarily active during nuclear division in the movement and differentiation of chromosomes. Microtubules make up spindle fibres.
The centromere is the chromosome's specialized DNA sequence linking a pair of sister chromatids. Spindle fibres bind through the kinetochore to the centromere during mitosis. Genetic loci that control the action of chromosomes were first thought to be centromeres.
(iii) The sister chromatids have separated each chromosome and migrated to the opposite poles.
(iv) Two
Note: Mitosis is responsible for an individual's growth and development. The constant number of chromosomes in all the cells of an organism's body is preserved by this process. It is important for asexual reproduction and vegetative propagation in plants and it is also responsible for damaged tissue repair and regeneration.
