Question
Question: The diagram given below is a representation of a certain phenomenon pertaining to the nervous system...
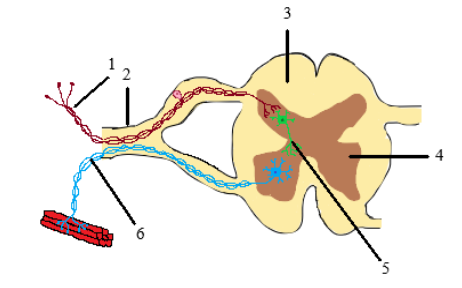
The diagram given below is a representation of a certain phenomenon pertaining to the nervous system. Study the diagram and answer the following questions.
(i) Name the phenomenon that is being depicted
(ii) Give the technical term for the point of contact between the two nerve cells
(iii) Name the parts 1, 2, 3, and 4
(iv) How does the arrangement of neurons in the spinal cord differ from that of the brain?
Solution
Reflexes are guided by a pathway called reflex arc. The main components of the reflex arc are sensory nerves that are activated and, in turn, bind to other nerve cells that activate the muscle cells or effectors that conduct a reflex action.
Complete answer:
The cells of the nervous tissue are known as neurons. A neuron consists of a cell body with cytoplasm and a nucleus, dendrites, axon, and nerve endings. The signals that pass along neurons of a nerve fibre is called a nerve impulse.
(i) The phenomenon that is being depicted is the reflex action. Reflex action occurs involuntarily and immediately in response to stimuli.
(ii) Nerve impulses can pass through several junctions from one neuron to another. Such junctions are known as synapses. So, the synapse is the point of contact between the two nerve cells.
(iii) 1- Sensory neuron 2- Dorsal ganglion 3- White matter 4- Grey matter
(iv) Gray matter is located on the outside and white matter on the inside of the brain. The inward portion of the cerebrum is considered white matter. It is mainly made up of long nerve cell fibres that transmit signals to and from the brain to the rest of the body. The fatty lining that covers the axons gives a white colour to this section of the brain. In the spinal cord, the white matter is found on the outside and grey matter on the inside.
Note: The response to stimulus cannot be adjusted or changed as per needs or circumstances. Reflex arc stimuli and motor response to the stimuli is a physiological component of the nervous system.
