Question
Question: The degree of dissociation of \( S{O_3} \) is \( \alpha \) at equilibrium pressure \( {P_0} \) . Wha...
The degree of dissociation of SO3 is α at equilibrium pressure P0 . What is Kp for the reaction 2SO3(g)⇄2SO2(g)+O2(g) ?
A) 2(1−α)3P0α3
B) (2+α)(1−α)2P0α3
C) 2(1−α)2P0α3
D) None of the above.
Solution
Hint : In the given reaction, Sulfur trioxide is dissociating to form Sulfur dioxide and Oxygen. The total pressure of this reaction is given as P0 so find the partial pressures of each compound. The formula of Kp is the ratio of partial pressures of products to the reactants.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Given to us is a reaction involving the dissociation of Sulfur trioxide to Sulfur dioxide and Oxygen. The equation for this reaction is written as 2SO3(g)⇄2SO2(g)+O2(g)
This is an equilibrium reaction. Let the initial partial pressure of Sulfur trioxide be P. We can now write a table showing the partial pressures of products and reactants initially and at equilibrium.
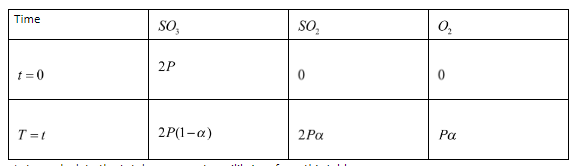
Let us calculate the total pressure at equilibrium from this table.
Ptotal=2P(1−α)+2Pα+Pα
By solving, we get Ptotal=2P−2Pα+2Pα+Pα=2P+Pα
It is already given to us that the total pressure at equilibrium is P0
By equating these two, we get P0=P(2+α) and we can write this as P=2+αP0
Now we write the formula of Kp for the given equilibrium reaction as follows:
Kp=[PSO3]2[PSO2]2[PO2]
By substituting the values of partial pressures of each component, we get Kp=(2P(1−α))2(2Pα)2(Pα)
On solving, we get Kp=4P2(1−α)24P3α3=(1−α)2Pα3
We have already found a relation between partial pressure P and total pressure P0 so let us substitute the value of P from that relation.
Now the above equation becomes Kp=(2+α)(1−α)2P0α3
Therefore the correct answer is option B.
Note :
It is to be noted that before writing the formula for Kp or drawing the table for partial pressures of the compounds, the reaction equation must be balanced. This is because Kp is dependent on the exponential values of the partial pressures.
