Question
Question: The decreasing order of \(pK_a\) value of the following is: 
A.III>I>II
B.II>I>III
C.I>III>II
D.I>II=III
Solution
The measure for a compound to define its tendency to donate protons is known as Ka value and the constant which describes the binding of protons is known as pKa . both of these constants are defined at the equilibrium.
Complete step by step answer:
To predict whether the acid will donate or withdraw protons, some constants such as Ka,pKa and Kb,pKb . The constants related to acids are Ka,pKa and the constants related to base are Kb,pKb. At equilibrium the acid constant is defined for an acid dissociation reaction, the acid dissociation constant is represented as Ka . It represents the strength of an acid and the power of its dissociation in solvent. But the pKa value is something different, it tells how tightly a proton is bound with the he acid. If the pKa value is lower then we can say that the binding of proton and the bronsted acid is not very strong and hence it is easy to donate protons. So we can say that if the pKa value is lower, acid is more acidic and if the pKa value is low then the acidic strength of acid is very low.
So, pKa value is inversely proportional to the acidic strength of a compound.
Now we will observe the order of acidic strength of these given compounds and the reverse of it will be the order of the pKa values.
And we all know that, the compound having more stable conjugate base will be more acidic, so we will see their conjugate bases which are as follows:
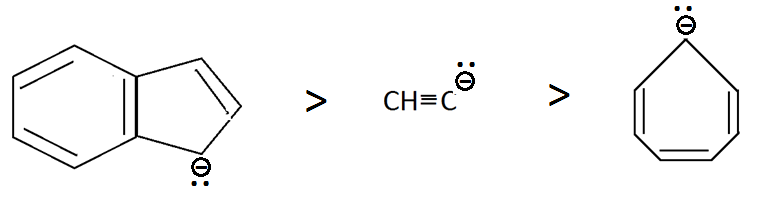
Compound III has aromatic stability due to resonance, compound II has negative charge on sp carbon atom and the first compound is anti aromatic so the order stability will be the same as shown above.
Therefore the order of acidic strength will be as follows:
III>I>II
And the order reverse to it will be the order of pKa values, therefore the order of pKa values, will be as follows:
II>I>III
Hence option (B) is correct.
Note: As we have discussed above that, the smaller the value of Ka , the larger the value of pKa and vice versa. But they have a unique relation between them mathematically also for numerical problems.
The relation is as follows: pKa=−log10Ka
