Question
Question: The cut-in voltage for silicon diode is approximately A. \[0.2\,{\text{V}}\] B. \[0.7\,{\text{V}...
The cut-in voltage for silicon diode is approximately
A. 0.2V
B. 0.7V
C. 1.1V
D. 1.4V
Solution
At first, recall the properties of a diode. Understand what cut-in voltage and forward biased voltage is. And then using the V-I characteristics graph, look for the cut-in voltage and compare with the given options and select the option which approximately matches with the value obtained from V-I characteristics graph.
Complete step by step answer:
A diode is a two terminal device which allows the flow of current in one direction only and the current flow in the opposite direction.The cut-in voltage is the forward biased voltage at which large electric currents start to pass through the diode.The most common type of diode used is p-n junction diode. There are two sides of a diode, p-side and n-side, in which the n-side electrons act as the charge carrier and in the p-side the holes act as the charge carriers. The region between p-side and n-side is known as the depletion region where the electrons diffuse from n-side to p-side to fill the holes. We can find out the cut-in voltage through V-I characteristics graph as shown below,
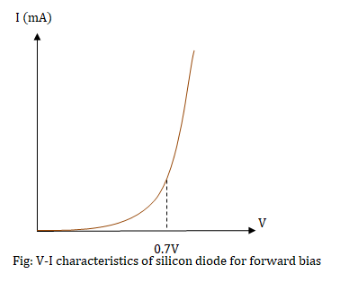
Here, V is the voltage across the diode and I is the current through the diode. We observe that at voltage, V=0.7V the diode starts allowing high currents to pass through it.Therefore, the cut-in voltage for silicon diodes is 0.7V.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: When the diode is forward biased that is when the p-terminal of the diode is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and then n-terminal of the diode is connected to negative terminal of the battery, the electrons easily flow from n-side to p-side and the diode conducts. But when in case of reverse biased, the p-terminal of diode is connected to negative terminal of the battery and n-terminal of the diode is connected to positive terminal of the battery, in this case the depletion region widens and the diode does not conduct.
