Question
Question: The current which changes direction after equal interval of time is known as...
The current which changes direction after equal interval of time is known as
Solution
A stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, flowing through an electrical conductor or space is known as an electric current. It's the net rate of electric charge flow through a surface or into a control container that's monitored. Charge carriers are the moving particles, and depending on the conductor, they might be one of numerous sorts of particles.
Complete step by step solution:
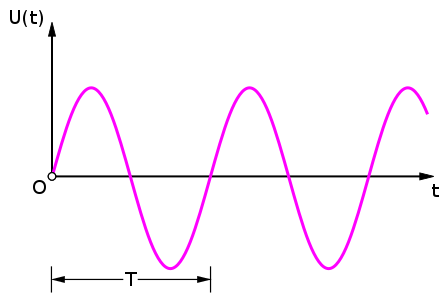

A current that varies its amplitude and polarity at regular intervals is known as alternating current. It may also be characterised as a current that changes or reverses its direction on a regular basis, as opposed to Direct Current (DC), which constantly runs in one direction, as seen below. We can observe from the graph that charged particles in AC tend to go from zero. It rises to its highest point before falling down to zero, completing one positive cycle. After that, the particles reverse their path and reach their maximum in the other direction, after which AC returns to its initial value, completing a negative cycle. The cycle is repeated over and over again.
Normally, alternating currents are accompanied by alternating voltages. Furthermore, alternating current may simply be converted from a higher to a lower voltage level. Alternators are devices that may be used to create or generate alternating current. Alternating current, on the other hand, may be generated in a variety of ways, including the use of several circuits. A basic single coil AC generator, which consists of two-pole magnets and a single rectangular loop of wire, is one of the most frequent or simple means of producing AC. The AC generator transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy using Faraday's concept of electromagnetic induction.
Note:
AC is the most common type of current found in household equipment. Audio signals, radio signals, and other forms of alternating current are examples. Alternating current has a significant benefit over direct current in that it can transport electricity across long distances with minimal energy loss.
