Question
Question: The covering or protective tissue in the animal body is (a) Connective (b)Epithelial (c ) Musc...
The covering or protective tissue in the animal body is
(a) Connective
(b)Epithelial
(c ) Muscular
(d)Nervous
Solution
Cells of the protective tissue are compactly arranged in one or more layers. They are held together by strong intercellular complexes. Little intercellular material between the cells is essential for their protective function.
Complete answer:
Epithelial tissue lines body cavities and forms glands. They occur on external and internal exposed surfaces of the body parts where they form a protective covering.
Additional Information:
Connective tissue is the most abundant and distributed widely in the body. Its function is to bind together different tissues or organs and support various structures of the animal body. E.g. Blood is a red coloured vascular connective tissue which transports oxygen and carbon dioxide. They also contain cells for generating immune responses and clotting.
Muscular tissue brings about movements of the body parts and locomotion of an organism through their special property of contractility.E.g. Skeletal muscles which are long, cylindrical with striations on their body. They are responsible for voluntary movements of our body.
Nervous tissue helps in the control and coordination of various body parts through their unique property of excitability and conductivity. They do so through neurons which respond to any stimuli and convey the nerve impulse generated.
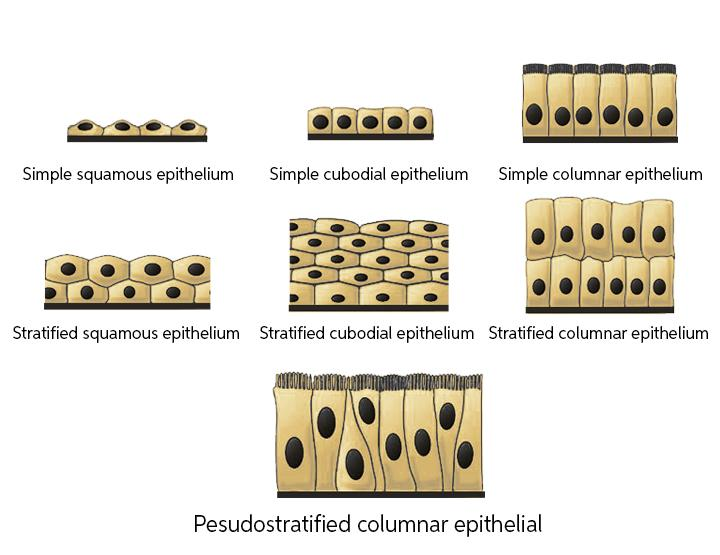
Depending on the number of layers of cells, epithelial tissues are of two types- simple or unstratified and compound or stratified. Based on shape, epithelial cells are divided into squamous, cuboidal, columnar and ciliated.
So, the correct answer is ‘Epithelial cells.’
Note: Some columnar and cuboidal cells are specialized for secretion. They are known as the glandular epithelium. They can be unicellular (E.g. Goblet cells in the alimentary canal) or multicellular( E.g. Salivary gland). The glands can be exocrine if secretion is poured through ducts or endocrine if secretions are poured directly into the blood.