Question
Question: The covalency of nitrogen in \( HN{{O}_{3}} \) is: (A) \( 0 \) (B) \( 3 \) (C) \( 4 \) (D...
The covalency of nitrogen in HNO3 is:
(A) 0
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
Solution
Hint : We know that covalence of an element is the number of bonds that an element makes within a compound or molecule. In HNO3 , nitrogen is attached to two oxygen atoms and one hydroxide ion as we can see from the structure of HNO3 and hence we have to count total bonds around nitrogen in HNO3 in order to know its covalence in HNO3 .
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The electronic configuration of nitrogen is 1s22s22p3 . The orbital 1s is completely filled and is present quite inside the shell and hence cannot be used in bonding. Only 2s and 2p orbitals are left. The formation of four bonds by nitrogen (or nitrogen having a covalency of four) can be explained by having a hybridization of sp3 by combination of 2s and 2p orbitals. Nitrogen uses its lone pair of electrons to have a covalence of four. The dot structure is given as;
⋅⋅O¨::N(:⋅⋅O¨:):⋅⋅O¨:H
Nitrogen having a covalency of three has a non-bonding or lone pair of electrons with it.
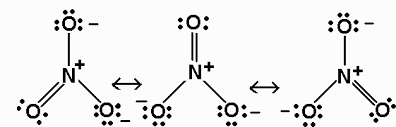 As we can see in the structure of HNO3 , nitrogen do not contain lone pair of electrons as a positive charge is present on nitrogen and hence the covalency of nitrogen is 4
As we can see in the structure of HNO3 , nitrogen do not contain lone pair of electrons as a positive charge is present on nitrogen and hence the covalency of nitrogen is 4
Hence, option C is the right answer.
Additional Information:
Since nitrogen does not possess d orbitals in its valence shell (n=2) , therefore it can show a maximum covalency of 4 and that too when it donates its lone pair of electrons. In other words, nitrogen cannot extend its covalence beyond 4 . That is why nitrogen does not form NF5orNCl5 .
Note :
It should be noted that phosphorus and other elements of the group 13 have empty d orbitals and can utilize all their valence orbitals to exhibit covalence of 5or6 . We should know the difference between oxidation state and covalency. The oxidation state of nitrogen in HNO3 is +5 while the covalency of nitrogen in HNO3 is four.
