Question
Question: The correct statement(s) about the compound \({{H}_{3}}C(HO)HCCH=CHCH(OH)C{{H}_{3}}\) (X) are: A. ...
The correct statement(s) about the compound H3C(HO)HCCH=CHCH(OH)CH3 (X) are:
A. The total number of stereoisomers possible for X is 6.
B. The total number of diastereomers possible for X is 3.
C. If the stereochemistry about the double bond in X is trans, the number of enantiomers possible for X is 4.
D. If the stereochemistry about the double bond in X is cis, the number of enantiomers possible foe X is 2.
Solution
To know about the cis or trans isomer first we should identify the compound has double bond in its structure or not. To know about the enantiomers and diastereomers of the compound we should know whether the molecule contains chiral carbon or not.
Complete answer:
- As per the question we have to find the correct statement related to the given compound.
- The given compound is H3C(HO)HCCH=CHCH(OH)CH3 .
- First we will find the number of chiral carbons present in the given compound by drawing the proper structure. The structure of the compound is as follows.
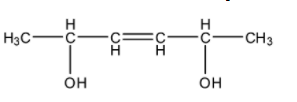
- In the structure find the chiral centers first.
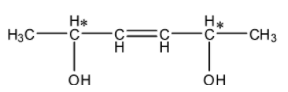
- The carbons which are marked with stars are chiral centers. Means there are two chiral centers present in the given compound.
- The given molecule can exist in cis or trans isomer due to the presence of a double bond.
- We can draw the cis and trans structures of the given compound as follows.
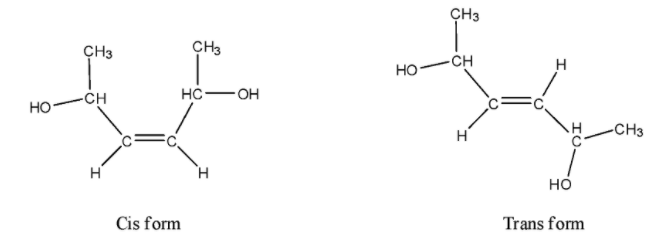
- We can write the various isomers formed by the given compound. They are as follows.
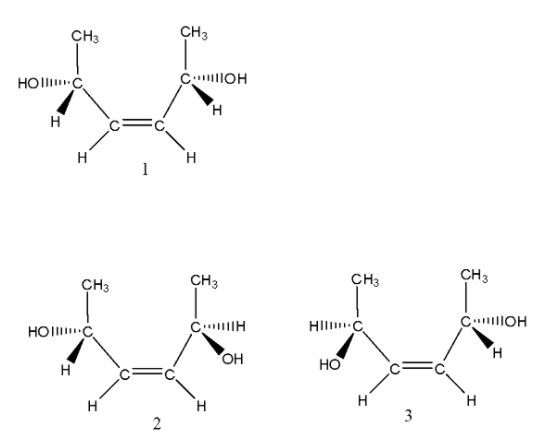
- In the above structures, structure 1 is an optically active molecule and has a plane of symmetry and structures 2 and 3 enantiomers.
- Coming to the trans structure, we can see as follows.
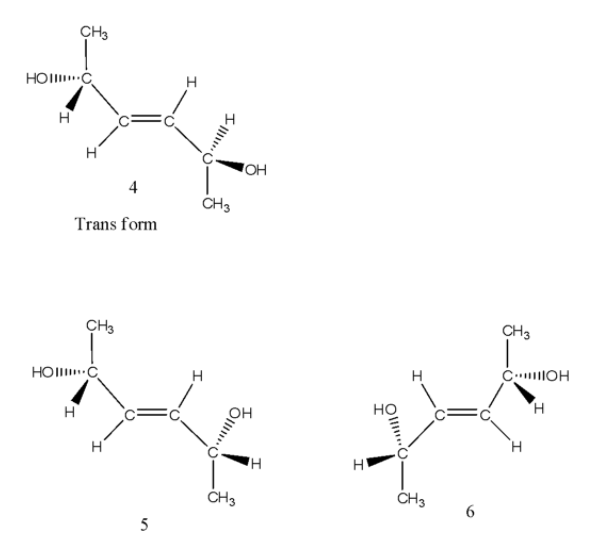
- The trans isomer has a center of symmetry and is optically inactive and structures 5 and 6 are enantiomers.
- Means the given compound has 6 stereoisomers. Then option A is correct.
- Coming to option B, the total number of diastereomers possible for X is 3. It is wrong because more than three diastereomers are going to form by C. They are (1,2) (1,3) (1,4)(1,5)(1,6) etc.
- Coming to option C, If the stereochemistry about the double bond in X is trans, the number of enantiomers possible for X is 4. But in the case of trans isomers we can see in the above structures (4,5,6) there are only two enantiomers are going to form. So, option C is wrong.
- Coming to option D, If the stereochemistry about the double bond in X is cis, the number of enantiomers possible foe X is 2. It is correct because from structure 1 (cis form) there are two enantiomers are going to form (2,3).
Therefore option A and D are correct.
Note:
While drawing the structures of cis and trans make sure that the substituents are arranged properly. Enantiomers are the molecules that show mirror images and are super impossible on one another. Diastereomers are the compounds which non-mirror images and non-superimposable on one another.
