Question
Question: The correct order of reactivity of \( I \) , \( \;II\; \) , and \( \;III\; \) towards addition react...
The correct order of reactivity of I , II , and III towards addition reaction is:
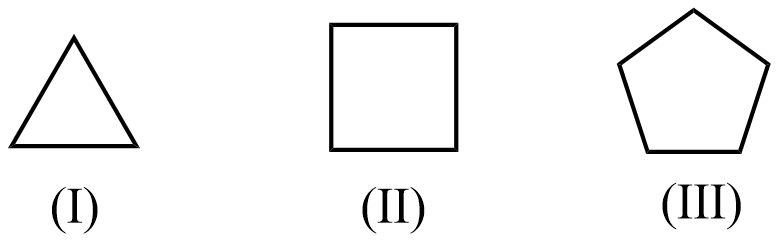
(A) I>III>II
(B) I>II>III
(C) III>II>I
(D) III>I>II
Solution
Addition reactions are mostly seen in the compounds that are less stable due to double or triple bond, due to carbon arrangement etc. Hence, from the above given three compounds, the compound which is the least stable, will be the most reactive towards addition reaction.
Complete answer:
From the given diagrams above, we can understand that (I) shows cyclopropane, (II) shows cyclobutane, (III) shows cyclopentane.
Now, additional reactions are the reactions in which a bond of a compound ( π bond for the alkenes and alkynes) is broken and by addition of a new element or molecule, a new hydrocarbon is formed.
The compounds that are most reactive towards additional reactions are the compounds that mostly have an unstable bond (e.g. π bond) or an unstable arrangement.
Hence, the unstable compounds are most reactive towards addition reaction, whereas stable compounds are already stable and do not need to make a new bond to increase stability and hence less reactive towards addition reaction
Hence, here we need to find the trend of increasing stability and the trend for reactivity will be inverse of it.
Now, let us consider Baeyer’s theory, which says “The four valencies of the carbon are directed towards the four corners of the tetrahedron” and hence, a natural and stable angle between the bonds of carbon is equal to the angle in tetrahedron which is 109∘28′ .
Hence, if the angle between bonds of carbon is equal to or more than 109∘28′ , then the structure will be stable.
Now, let us consider cyclopropane in which the angle between the bonds of carbon is 60∘ . This value is very less than the stable values, and hence the carbon bonds will be strained and will tend to increase the angle between the bonds.
If cyclopropane is reacted with a molecule like bromine or chlorine, the ring will break and one atom will get attached at both ends, which is known as 1,3−dibromidepropane or 1,3−dichloridepropane , which is a linear compound and angle between bonds will be almost 180∘ . Thus, cyclopropane is the most reactive towards the addition reaction, as the strain in angle is the maximum.
Considering cyclopentane, the angle between the bonds will be equal to 108∘ which is very near to the stable angle value, and hence the strain in the arrangement will be very less. Hence, cyclopentane is already stable and the least reactive towards addition reaction for changing structural arrangement.
Hence, the stability trend is III>II>I and the reactivity trend will be inverse i.e. I>II>III
Hence, the correct answer is Option (B) .
Note:
From this question, we can observe a trend of increasing stability and decreasing reactivity towards additional reaction. Hence, as we go towards higher order cycloalkanes, as the angle between the bonds increases, the stability increases, and the reactivity towards addition reaction decreases. Also, as a fact higher order cycloalkanes do not undergo addition reaction, instead they follow substitution reactions.
