Question
Question: The correct explanation for the part shown by the arrow is that A. It is the hydrophilic B. It ...
The correct explanation for the part shown by the arrow is that
A. It is the hydrophilic
B. It forms the outer layer of the plasma membrane
C. It is composed of phosphate atoms
D. It contains nonpolar covalent bonds
E. It is capable of hydrogen bonding
Solution
Cells consist of distinct characteristics such as a nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, and other cell organelles. The plasma membrane also known as the cell membrane segregates and protects the internal constituents of the cell from the external environment.
Complete answer: In the framework of this question, the part focused with the arrow represents the double phospholipid layer, termed as the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane. The lipid bilayer is semipermeable and consists of a head and two tails. The head is composed of a phosphate group whereas the tails consist of fatty acids. The head is hydrophilic in nature, i.e. it is solvent-loving and is attracted to water. However, the tails of the phospholipids are hydrophobic, i.e. solvent-hating, and are repelled by water. The phospholipid head is pointed towards either the cytoplasm or the fluid surrounding the cell. Whereas, the tail is situated inside the membrane.
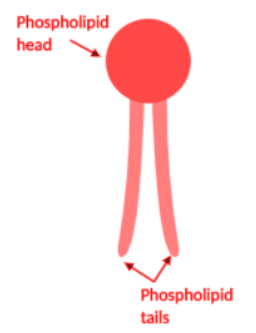
One of the major functions of the cell membrane is the transport of selective molecules and ions in and out of the cell. Since the phospholipid tails constitute the interior of the membrane, hence they allow the effortless passage of hydrophobic small molecules through the plasma membrane. Hydrophilic molecules cannot pass across the cell membrane, except when they bind to a carrier protein and undergo facilitated diffusion. The hydrophobic phospholipid tails are bound with non-polar covalent bonds, which are also observed within the plasma membrane.
Hence, the correct answer is option D, i.e., It contains nonpolar covalent bonds.
Note: The plasma membrane comprises glycoproteins and lipoproteins which interact with the molecules and ions of other cells. Other functions of a plasma membrane include providing structural support to the cell.
