Question
Question: The correct bond order in which the \({\text{O}} - {\text{O}}\) bond length increases as: A. \({{\...
The correct bond order in which the O−O bond length increases as:
A. H2O2 < O2 < O3
B. O3 < H2O2 < O2
C. O2 < O3 < H2O2
D. O2 < H2O2 < O3
Solution
Bond length is the distance between the bonded atoms. Bond length depends upon the bond strength and bond order. As the bond strength or bond
order increases the bond length decreases.
Complete step by step answer:
The bond length depends upon the bond strength which in turn depends upon the bond order. As the bond order increases the bond strength increases which in turn decreases the bond length.
So, the relations in bond length, bond order, and bond strength are as follows:
B.L.∝B.O.1∝B.S.1
Where, B.L. is the bond length, B.O. is the bond order and B.S. is the bond strength.
The structures of all three molecules are as follows:
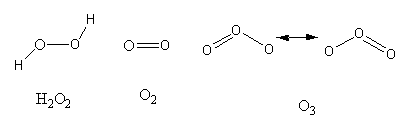
The O−O chemical bonds in H2O2 is one, in O2 is two and in O3 is in-between one and two because in O3 some resonating structures are possible which are interconvertible.
So, the decreasing order of bond order or bond strength is,
O2>O3>H2O2
Bond order is inversely proportional to bond length so, the increasing order of bond length is,
O2 < O3 < H2O2
Therefore, option (C) O2 < O3 < H2O2 , is correct.
Note: Bond order is defined as the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. Bond length is inversely proportional to the bond strength and bond order. Bond strength is directly proportional to the bond order. If the structure is known then the bond order is determined by the molecular orbitals diagram. The formula used to determine the bond order is as follows: 2bondingelectron−antibonding electron .
