Question
Question: The confirmatory test most commonly used to diagnose AIDS is A. ELISA B. Western blot C C. ...
The confirmatory test most commonly used to diagnose AIDS is
A. ELISA
B. Western blot C
C. ESR
D. PCR
E. None of the above
Solution
AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome where HIV infects the immune cells. This causes faulty immune cell production and ultimately renders the human body vulnerable to fend off even the smallest infection.
Complete answer:
The Human Immunodeficiency Virus belongs to a class of retrovirus which is capable of replicating within the immune cells using a specific enzyme called reverse transcriptase. This virus has a specific receptor that allows it to attach to the T-cells of the immune system. As T-cells are the primary identifier and signaling cell which performs a majority of the immune function, damage to these cells causes impaired immunity. This virus is capable of remaining dormant in individuals for several years without showcasing any symptoms. Therefore, the only confirmatory test used to detect AIDS is ELISA. ELISA stands for Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay. This is an assay involving antibodies and an enzyme-linked antibody capable of producing color from a chromophore.
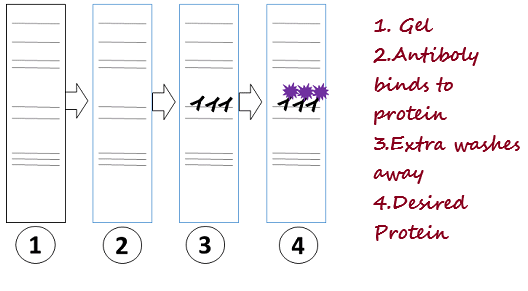
The main principle behind ELISA is that, when a blood sample containing the virus is exposed to antibodies with a specific receptor for the virus, the antibodies attach themselves to the virus. Depending on the type of ELISA used the primary or the secondary antibody is linked with an enzyme that is capable of producing color from a substrate. Thus, when the antibody is bound to the virus and the substrate for the enzyme is given it will create a distinct color. If there is no virus, the antibody would not bind and there would be no color produced as there is no enzyme-linked antibody present. There are several types of ELISA such as a direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive ELISA.
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note: Western blot is a technique used to determine the presence of a specific protein present in a given sample. It involves the use of protein-specific antibodies that bind to the protein and is identified by using a secondary antibody linked to an enzyme or radioactive compound. The major difference is that ELISA is much more specific than western blotting as multiple proteins can have a similar structure capable of binding with the protein antibody.
