Question
Question: The compound (F) is  is
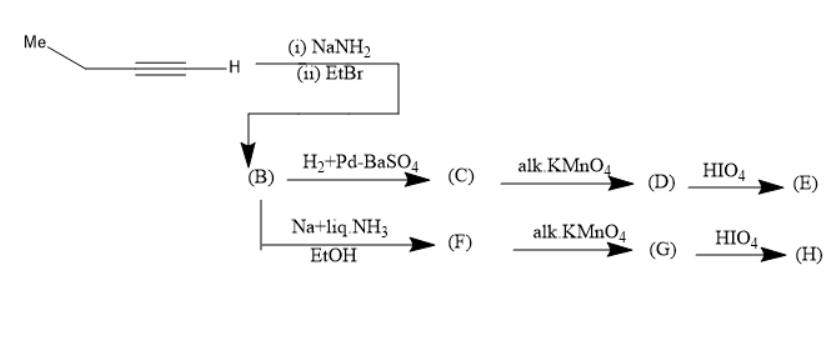
A)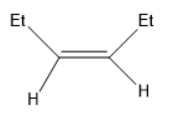
B)
C)
D) Both A and B
Solution
Alkynes on treatment with sodamide and alkyl halides gives alkyl substituted alkynes.
The alkyne on reduction with hydrogen forms alkenes while treatment with sodium in liquid ammonia forms trans alkenes. Alkenes with alkaline potassium permanganate forms diols, and diols treated with periodic acid form carbonyl compounds.
Complete answer: Given compound is 1- Butyne (A).
When this compound is treated with NaNH2 and EtBr forms ethyl substituted alkyne B.
B has the molecular formula of (C2H5)C≡C(C2H5)
When B is treated with Na+liq.NH3in EtOH forms trans alkene (F).
(F) has the molecular formula of (Et)CH=CH(Et).
In the compound (F)the two ethyl groups are attached to the double bonded carbons at opposite sides. Thus, it is a trans alkene.
The compound B on treated with hydrogen gas in presence of palladium in Barium sulphate (H2,Pd+BaSO4) forms cis alkenes, further treatment with alkaline potassium permanganate (alk.KMnO4) forms cis diols, on further treatment of cis-diols with periodic acid (HIO4) forms two molecules of propionaldehyde.
The compound Bon treated with hydrogen gas in presence of palladium in Barium sulphate (H2,Pd+BaSO4) forms trans alkenes, further treatment with alkaline potassium permanganate (alk.KMnO4) forms trans diols, on further treatment of trans-diols with periodic acid (HIO4) forms two molecules of propionaldehyde.
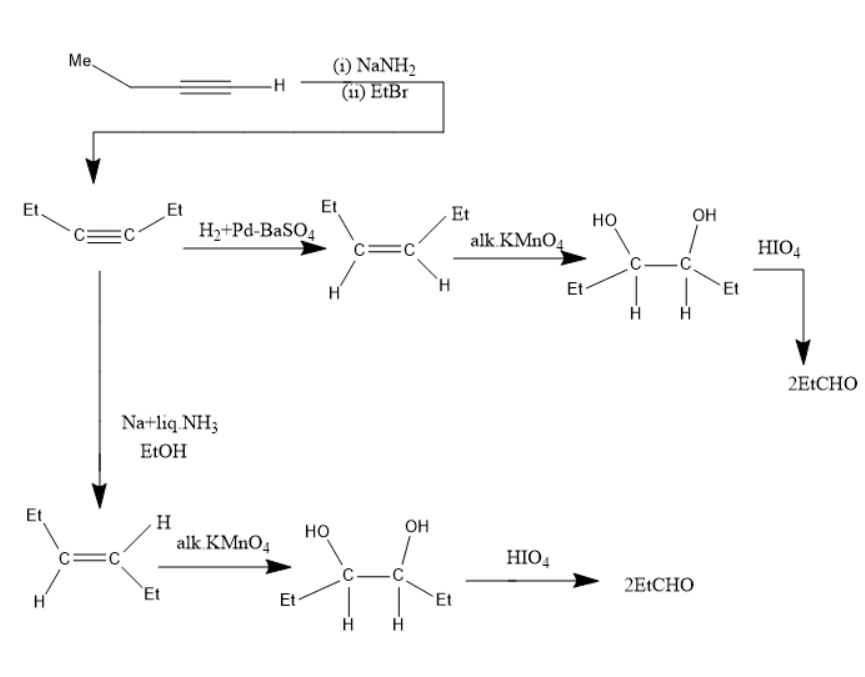
Thus, the compound F will be a trans alkene in which the two ethyl groups are oppositely attached to the double bonded carbon.
Sodium in liquid ammonia directs the alkynes to form trans alkenes.
Thus, Option (B) is the correct One.
Note:
Both sodium in liquid ammonia and hydrogen gas are used for the reduction of alkynes to alkenes.
But, the formation of products were geometrical isomers.
In both the cases, only gain of hydrogen takes place which can be termed as reduction.
