Question
Question: the combination of two layers of opposite charges around the colloidal particle is called Helmholtz ...
the combination of two layers of opposite charges around the colloidal particle is called Helmholtz electrical double layer. The potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opposite charge is called.
A.Electrode potential
B.Zeta potential
C.Absorption potential.
D.Diffused potential
Solution
first we know about the electrical double layer, the surface of a colloidal particle acquires positive or negative charge by selective absorption. The absorbing layer then attracts counter on from the medium, which forms the second layer of opposite charge. Thus an electrical double layer is developed.
Complete step by step solution:
Now we should first discuss the following important terms that should be known before giving the answer to the above question.
Helmholtz double-layer:
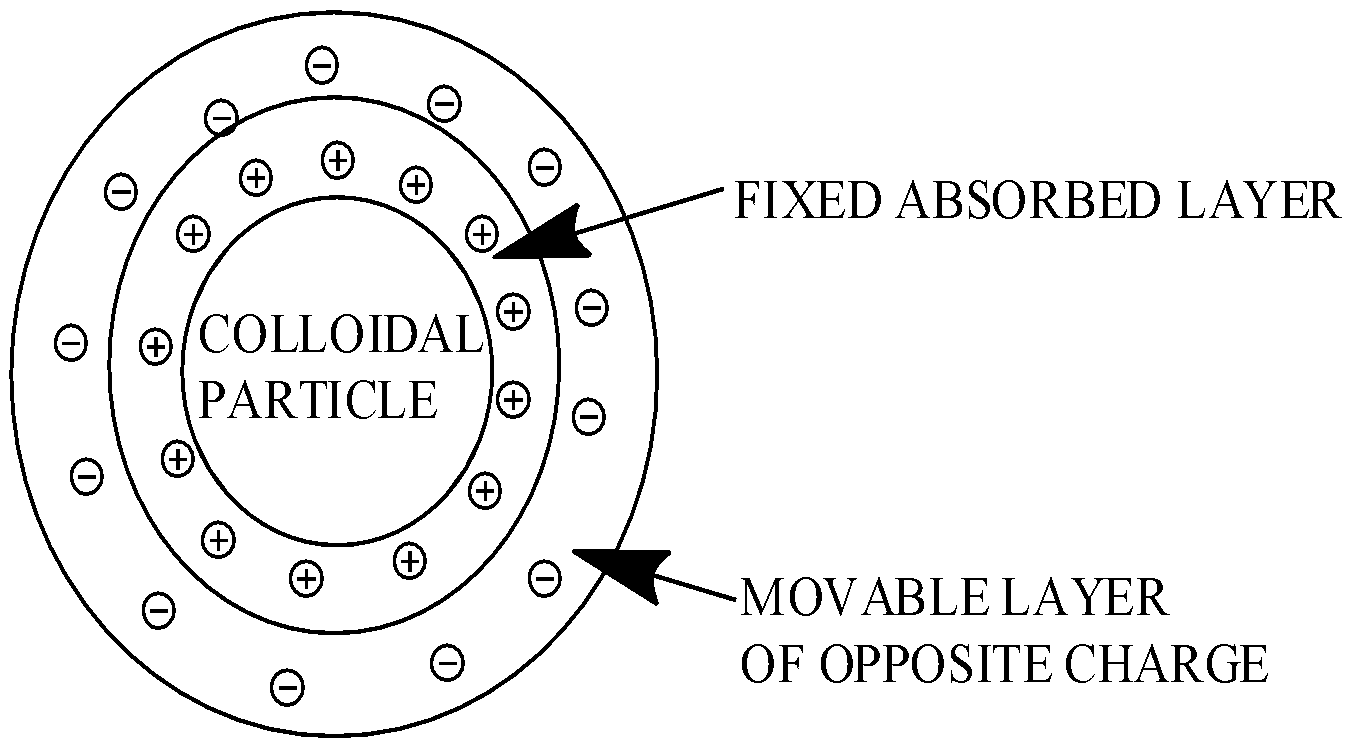
The combination of two layers of positive charges around the colloidal particle is called a Helmholtz double layer.
Stern’s double-layer:
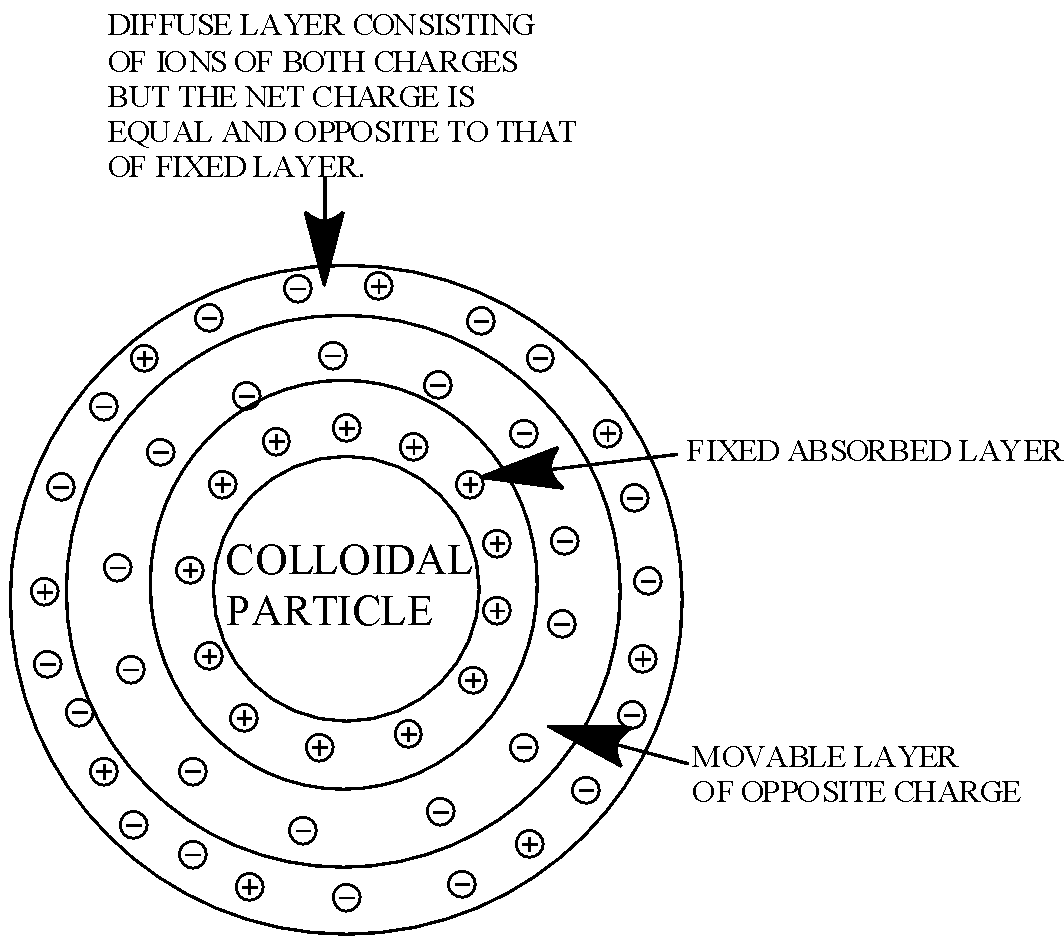
The double-layer proposed by Stern consists of two parts, one which is fixed at the particle surface and the second, which is mobile and diffused extending into the solution. The resultant charge of the diffuse layer is equal in magnitude but opposite sign to that of fixed layers. The potential difference between the fixed part and the diffuse part is known as zeta potential.
So the correct option of the given above question is known as zeta potential.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note: in the undistributed condition there exists a sharp drop of potential from the solid surface to the fixed part of the double layer on the solution side. It is followed by a gradual change in potential across the diffuse part up to the bulk of the solution.
Zeta potential is defined as the difference in the potential between the fixed layer and solution in bulk across the diffuse layer.
