Question
Question: The color of ppt A, B, and C respectively is? 
A. Black, yellow, deep yellow
B. Black. red, white
C. Brown, red, white
D. Black, white, red
Solution
Precipitate is basically the creation of a solid form of solution. The chemical which forms the solid is called the precipitate. If an ion is insoluble based on solubility, then it forms a solid(precipitate) with an ion from the other reactant present. While if all the ions in a reaction are soluble, i.e. they will remain in aqueous ion form, then no precipitation will occur.
Complete step by step answer:
When silver nitrate and sodium sulfide react with each other, the black color precipitation of Ag2S is formed. The reaction is shown below.
AgNO3+Na2S→Ag2S+NaNO3
When silver nitrate and potassium chromate reacts with each other, yellow color precipitation ofAg2CrO4 is formed. The reaction is shown below.
2AgNO3+K2CrO4→2KNO3+Ag2CrO4
When silver nitrate and potassium iodide reacts with each other, deep yellow color precipitation of AgI is formed. The reaction is shown below.
AgNO3+KI→KNO3+AgI
According to reaction, the reactions are,
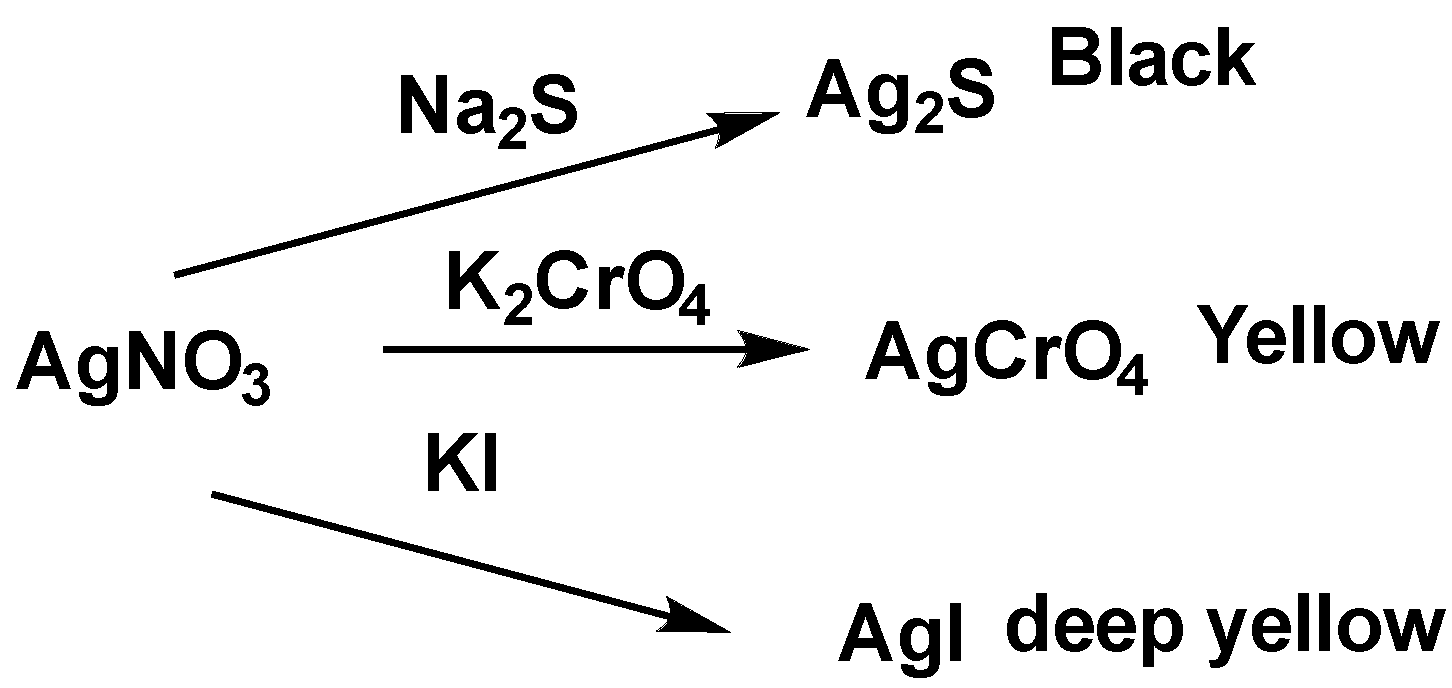
So, the correct option is A.
Additional Information:
An aqueous solution of magnesium chloride and silver nitrate when mixed results in the formation of solid silver chloride and aqueous magnesium nitrate.
We can express this reaction in terms of the molecular equation. It is a balanced chemical equation having molecules rather than ions with subscripts indicating the nature of the compound.
This gives us a balanced molecular equation-
MgCl2(aq)+2AgNO3(aq)→2AgCl(s)↓+Mg(NO3)2(aq)
Note:
The solubility of silver halides is dependent on the ionic size and hydration energy of the halides in the salts. If more energy is released upon hydration than there is stored in the ionic solid lattice, then solubility is favored. If there is a net gain of energy, i.e., if less energy is released on hydration than is stored in the ionic solid lattice, then solubility is unfavored. As we move down the period, Hydration energy decreases. Hence solubility also decreases as we move down a period. Hence, the trend for solubility in halides due to hydration energy can be shown as:
F−<Cl−<Br−<I−
Hence, the decreasing order of solubility of silver halide is:
AgF > AgCl > AgBr > AgI
