Question
Question: The basic theory behind Arrhenius equation is that: (A) The number of effective collisions is prop...
The basic theory behind Arrhenius equation is that:
(A) The number of effective collisions is proportional to the number of molecules above certain threshold energy.
(B) As the temperature increases, so does the number of molecules with energies exceeding the threshold energy.
(C) The rate constant is a function of temperature.
(D) The activation energy and the pre-exponential factor are always temperature independent.
Solution
Arrhenius equation is a relation between rate constant and temperature. It is applicable to gas molecules and gives the idea that as temperature increases the rate increases in a chemical reaction. It can be made up for two rate constants and then we can easily find the rate changes. Also according to the law of chemical kinetics, the rate of a chemical reaction depends upon the temperature, higher will the temperature, faster the reaction will proceed towards the product formation.
Complete step-by-step answer: Arrhenius equation is used to determine the relationship between the temperature and the rate at which the reaction will proceed. The expression gives us a relationship between the rates constant, the absolute temperature, and the A factor which is also called the pre-exponential factor. It gives us a clearer picture of the dependency of the rate of reaction on temperatures. As you know at higher temperatures, the chances of collisions of two molecules are higher. This high rate of collision results in higher kinetic energy, which further affects the activation energy of the reaction. The Arrhenius equation is given by the expression:
k=AeRT−Ea−−−−−−−(1)
Where, k= the rate constant of the reaction,
A= The pre-exponential factor, according to the collision theory, is the frequency of successful collisions between the reacting molecules.
Ea= The activation energy of the chemical reaction (energy per mole).
R= Universal gas constant, T= absolute temperature (in Kelvin)
The activation energy required by the molecule comes from the surrounding and the Pre-exponential factor is always constant for every reaction. Hence, both of these factors are independent of temperature. Therefore, we can say that rate is a function of temperature as it depends on temperature only.
If we take ln on both side we get this equation and now we can plot a graph between lnk versesT1, lnk=lnA−RTEa
Graph can be seen as we get a straight line
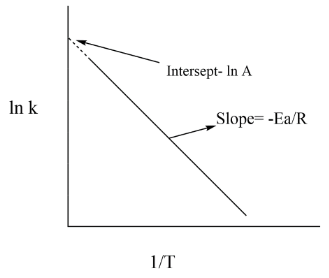
We get the equation as above, slope is given as REa and intercept as lnA
Hence, all the given options are correct.
Note: Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required by the atoms or molecules to participate in the reaction. They pass through the transition state having high activation energy. After the transition state the reactant molecules form products which have lower energy in case of exothermic reaction and higher for endothermic. The Arrhenius equation was given by Svante Arrhenius in 1889 . It has a vast application in determining the rate of reaction.
